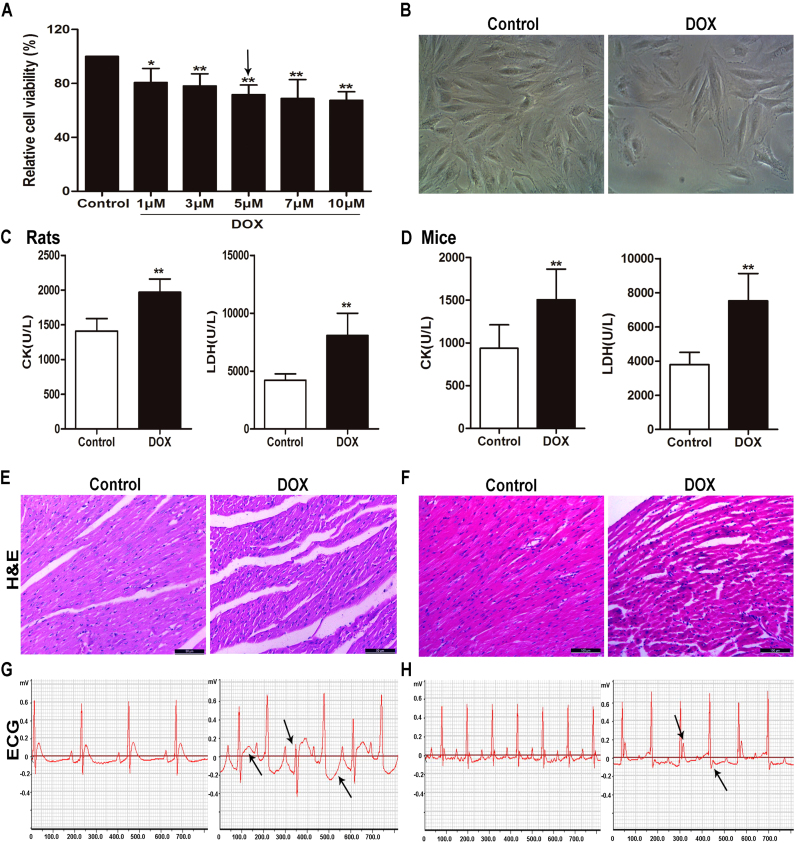
Fig. 1.
DOX causes myocardial injuryin vitroandin vivo. (A) The viability of H9C2 cells treated by DOX. (B) The morphology of H9C2 cells treated by DOX. (C) Serum levels of CK and LDH in rats caused by DOX. (D) Serum levels of CK and LDH in mice caused by DOX. (E) HE staining images of heart tissues in rats treated by DOX (×200 magnification). (F) HE staining images of heart tissues in mice treated by DOX (×200 magnification). (G) Electrocardiograms of rats treated by DOX. (H) Electrocardiograms of mice treated by DOX. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 5 for in vitro test and n = 10 for in vivo test). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with control group.