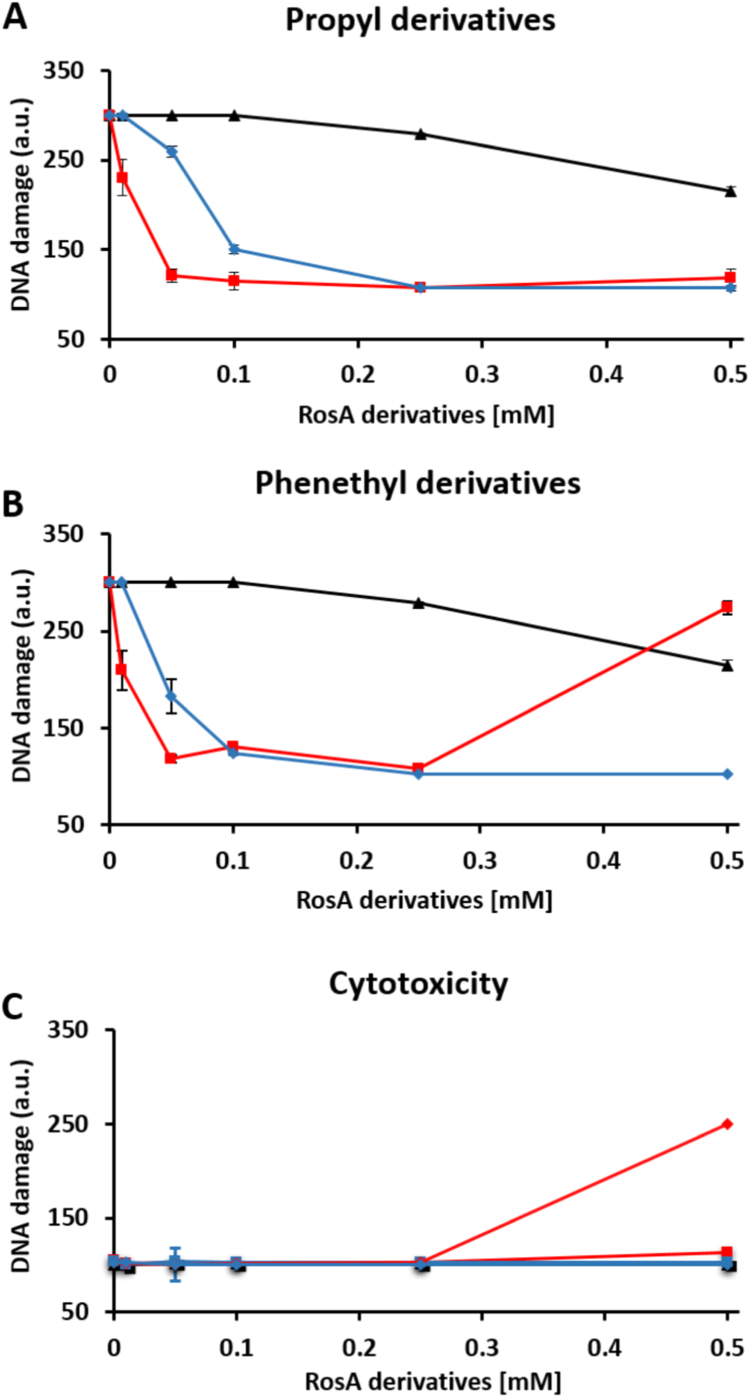
Fig. 2.
Protective effects offered by RosA-ester and RosA-amide derivatives against H2O2-induced DNA damage. Jurkat cells in culture (1.5 × 106 cells/ml) were pre-incubated for 20 min with the indicated concentrations (10, 50, 100, 250 and 500 μM) of RosA (black line) and RosA-propyl ester or RosA-propyl amide (red and blue lines, respectively) (A), or RosA, RosA-phenethyl ester or RA-phenethyl amide (black, red and blue lines, respectively) (B) and then exposed to an amount of glucose oxidase (0.6 μg/ml) able to generate about 10 μM H2O2 per minute. After 10 min of exposure to H2O2, cells were collected and analyzed for formation of single-strand breaks in their DNA by using the comet assay methodology. (C) Cells were treated with the tested compounds, as in (A) and (B), but were not exposed to H2O2. Formation of single-strand breaks in their DNA was measured by using the comet assay methodology. DNA damage was expressed in arbitrary units (a.u.), as described under Materials and Methods. Each point represents the mean ± SD of duplicate measurements in two separate experiments.