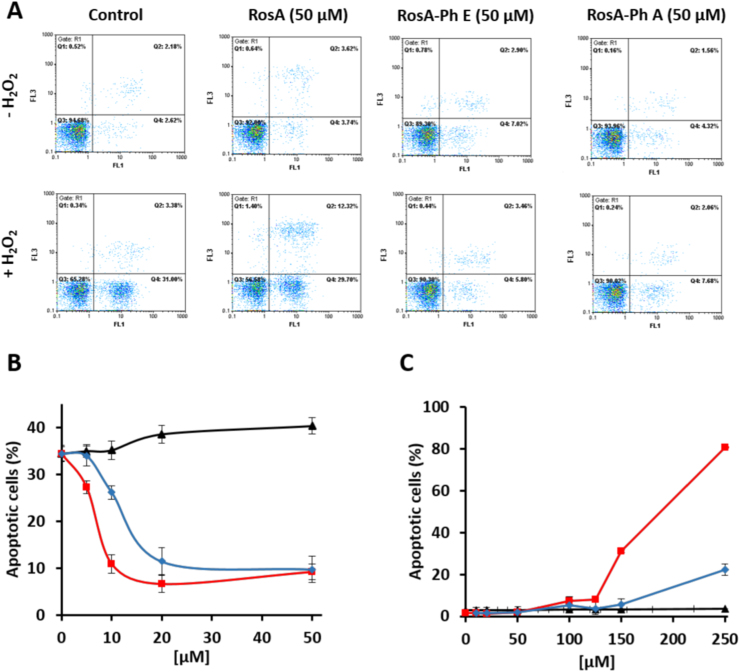
Fig. 5.
Protection against H2O2-induced apoptosis offered by RosA-phenethyl ester and RosA-phenethyl amide derivatives. (A) Jurkat cells (1.5 × 106 cells/ml) were incubated with 50 μM of the indicated compounds for 30 min before the addition of vehicle (upper panels) or 250 μΜ H2O2 (lower panels). Apoptotic cell death was evaluated 7 h later by flow cytometric analysis of Annexin-V binding cells (horizontal axis) and PI staining (vertical axis). (B) The experiments were performed as in (A), except that the indicated concentrations of the tested compounds (5, 10, 20, and 50 μΜ) were added into the culture medium 30 min before the addition of the H2O2. (C) Conditions were as in (A), except that H2O2-treatment was omitted. Quantification of apoptotic cells in (B) and (C) was performed by summing the counts of Annexin V-binding cells in Q4 (early apoptotic cells) plus Q2 (late apoptotic cells). Black, red and blue lines depict RosA, RosA-ester and RosA-amide derivatives, respectively. Bars represent the mean percentage of Annexin-V positive cells ± SEM from three independent experiments.