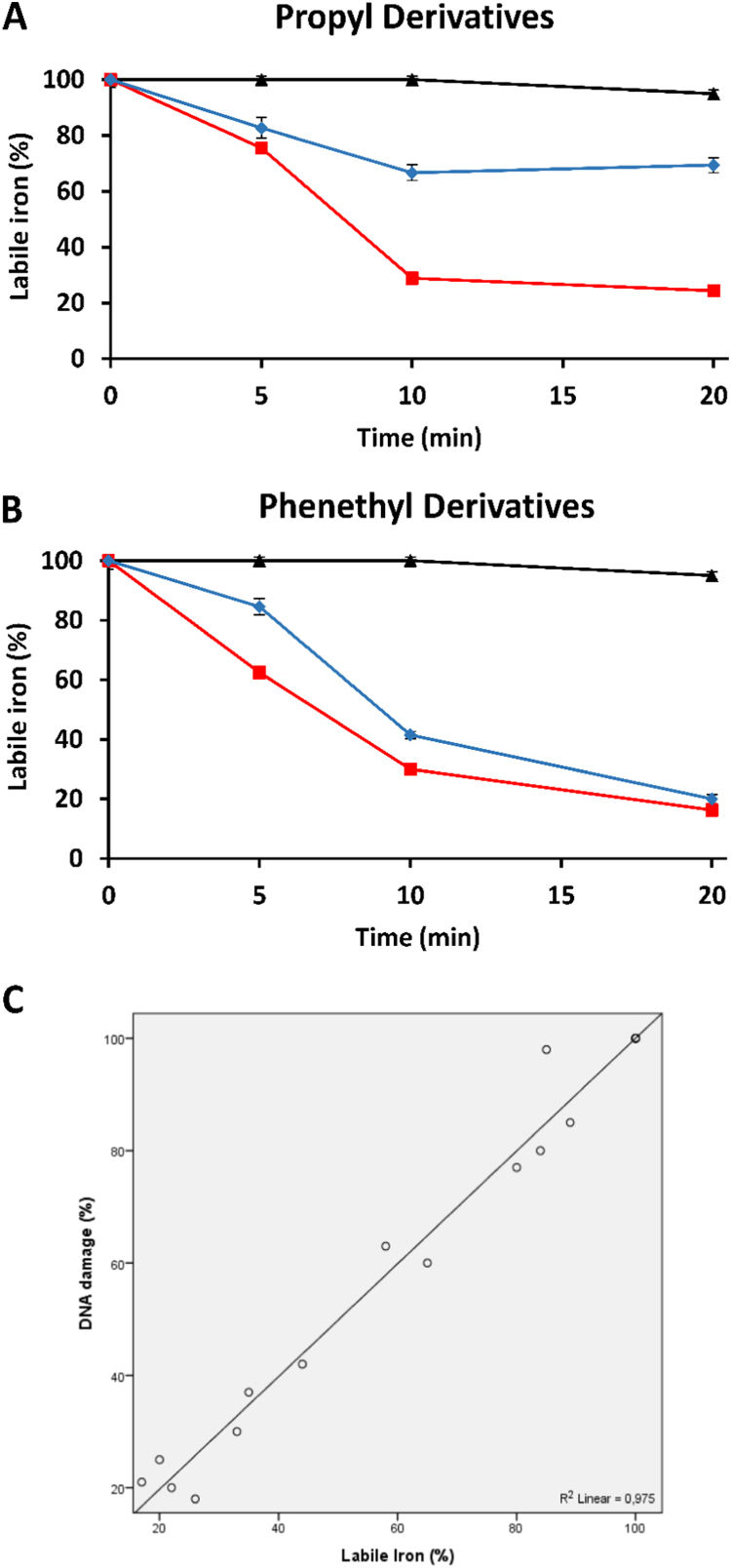
Fig. 6.
Capacity of RosA-ester and RosA-amide derivatives to chelate intracellular labile iron. The intracellular labile iron level in Jurkat cells was measured by using the calcein method, as described in Materials and Methods. RosA and its propyl (A) and phenethyl (B) ester and amide derivatives at the indicated concentrations were added directly into the cuvette of the fluorometer and the increase in fluorescence was monitored continuously. At the indicated time points (5, 10, 20 min), 11 μM SIH (a membrane-permeable and specific iron chelator) was added and any further fluorescence increase was recorded in order to estimate the percentage of iron still remaining bound to calcein. Black, red and blue lines depict RosA, RosA-ester and RosA-amide derivatives, respectively. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (C) Correlation between the protection offered by RosA derivatives against H2O2-induced DNA damage, as estimated by the comet assay, and its ability to decrease intracellular labile iron (r = 0.975, p < 0.001).