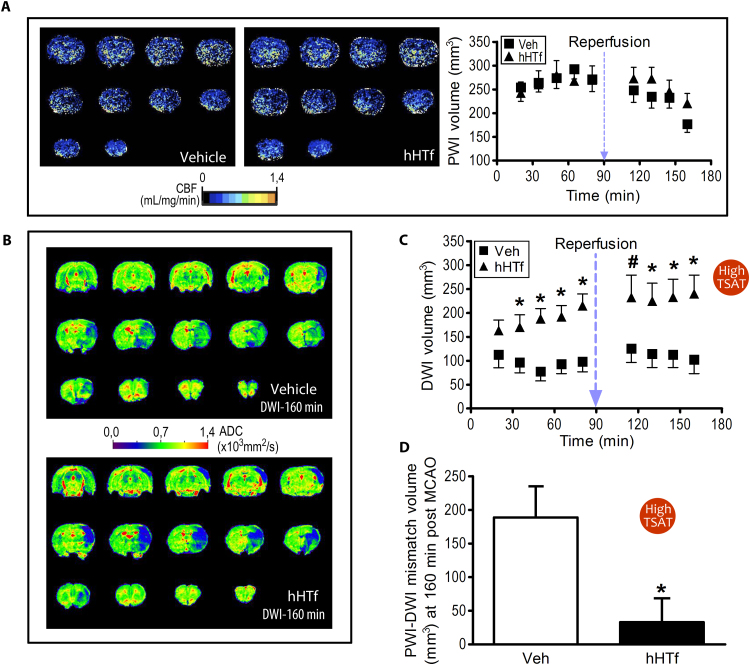
Fig. 4.
Experimentally-induced High TSAT with hHTf increases brain damage volume in rats exposed to tMCAO. (A) Representative MRI-PWI coronal sections of rat brains 70 min after ischemia onset (tMCAO by intraluminal thread) in Veh-treated (left) and hHTf-treated rats (middle). Time-course effect of hHTf-High TSAT on hypoperfused-PWI brain volume during ischemia and early reperfusion (right) (n = 8–12 per group). (B) Representative ADC maps obtained from DWI of coronal rat brain sections of tMCAO rats (Vehicle, top; hHTf-treated, bottom) 160 min after the ischemia onset. (C) Time-course effect of hHTf-High TSAT on lesion-DWI volumes during ischemia and early reperfusion (n = 8–12 per group; t-test: *p < 0.05, #p = 0.0563 vs respective Veh). (D) Salvageable hypoperfused brain tissue as assessed by PWI-DWI mismatch 160 min after the ischemia onset in normal TSAT (Veh) and High TSAT (hHTf) rats (n = 8–12 per group; t-test: *p = 0.0216).