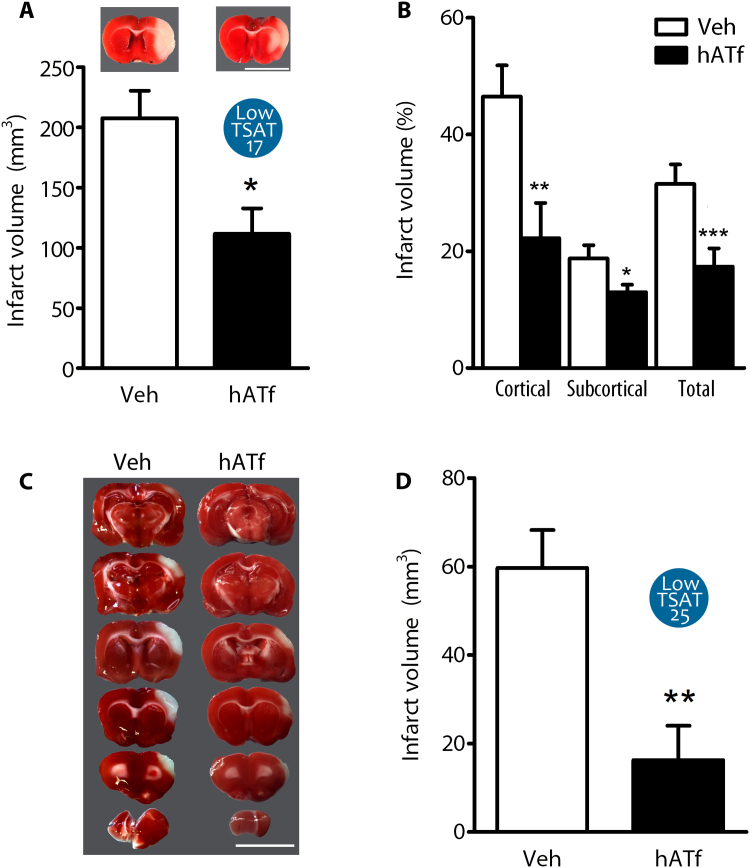
Fig. 5.
Experimentally-induced Low TSAT at reperfusion reduces the infarct volume in tMCAO rats. (A) Effect of reduction of TSAT to 17% (Low TSAT-17) by the administration of 300 mg/Kg hATf i.v. at reperfusion on the infarct volume (TTC staining) of tMCAO rats (intraluminal filament model); scale bar, 1 cm (n = 6–7 per group; t-test: *p = 0.0103). Representative TTC-stained brain slices are shown on top of each bar. (B) Effect of Low TSAT-17 on % infarct volume in cortical and subcortical brain regions (n = 6–7 per group; t-test: *p = 0.0436, **p = 0.0133, ***p = 0.0102 vs respective Veh). (C) Representative TTC-stained brain sections of rats treated at reperfusion with Veh or 200 mg/Kg hATf (Low TSAT-25), 24 h after tMCAO (ligature model); this model infarcts only cortical areas; scale bar, 1 cm. (D) Quantification of the effect of treatment with 200 mg/Kg hATf in the tMCAO model indicated in (C) (n = 6–7 per group; t-test: **p = 0.0036).