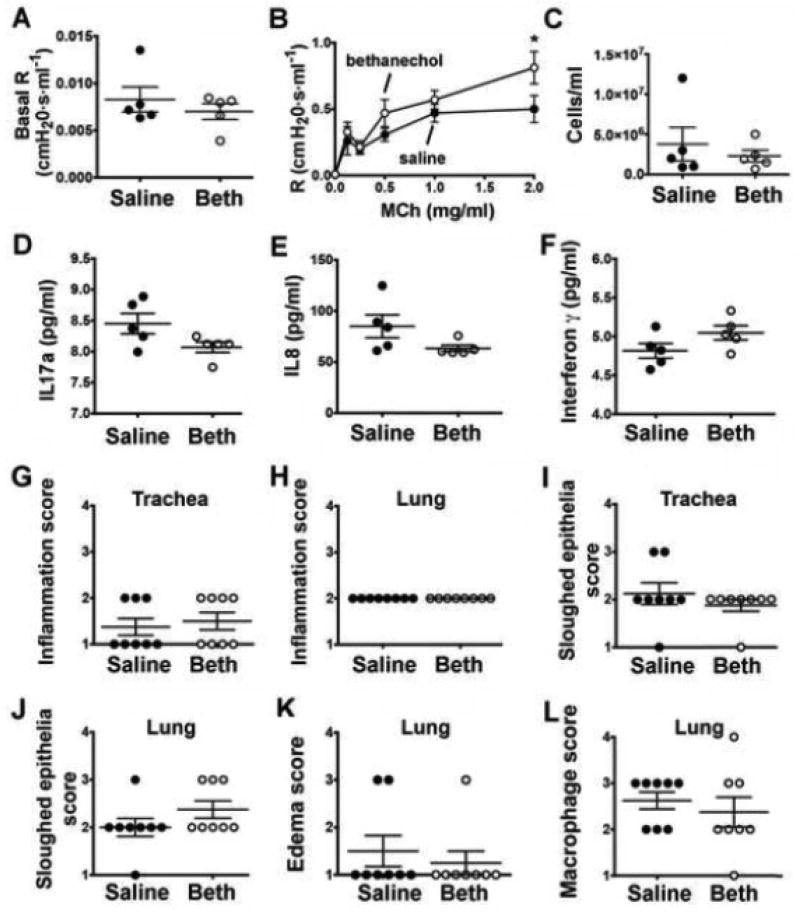
Figure 1.
Airway resistance and inflammation markers in neonatal piglets forty-eight hours post bethanechol challenge. (A) Baseline airway resistance prior to administering methacholine. (B) Airway resistance in response to increasing doses of methacholine; n = 5 piglets each group. (C) Number of cells/ml observed in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of saline-treated and bethanechol-treated piglets. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid concentrations of IL17A (D) IL8 (E) and IFNγ mediated. Histological scoring by a pathologist masked to treatment for inflammation (G, H), sloughed epithelium (I, J), edema (K) and macrophages (L). Scoring parameters for inflammation, edema and sloughed epithelium are as follows: 1= within normal limits; 2 = mild, uncommon, focal; 3 = moderate, multifocal; 4 = extensive, coalescing changes. Scoring parameters for macrophages are as follows: 1= within normal limits; 2 = accumulation within airway (<33%); 3 = accumulation within airway (34–66%); 4 = accumulation within airway (>67%). For panels A-F, n = 5 piglets per group; for panels G-L, n = 8 piglets per group. Data are mean ± SEM. For *, p < 0.05 for treatment effect using a two-way ANOVA. An unpaired Student’s t-test was used to assess basal airway resistance and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cells cytokine concentrations. A non-parametric Mann Whitney test was performed to examine histological scoring. All tests were carried out using Prism 7.0a. Abbreviations: R, resistance; MCh, methacholine; Beth, bethanechol; IL17a, interleukin 17a; IL8, interleukin 8; CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine 10; IFNγ, interferon gamma.