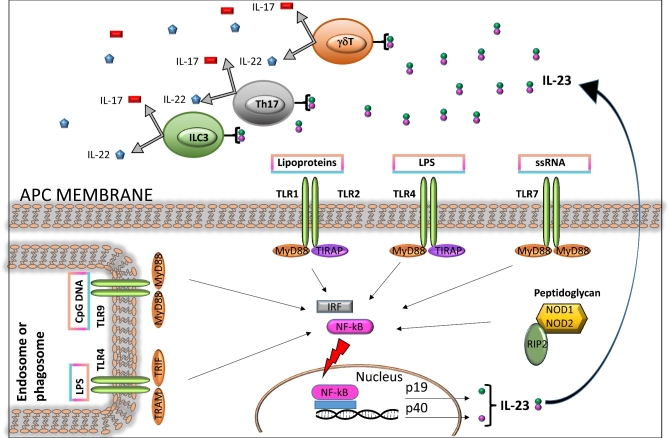
Figure 1.
Bacterium-induced signaling in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) leads to IL-23 production and subsequent activation of IL-17 and IL-22-producing cells. APCs, for instance DCs and macrophages, express PRRs on their surface, such as TLRs, and intracellular receptors in their cytosol, such as NLRs. These PRRs recognize conserved microbial-associated molecular motifs and PAMPs, including LPS, lipoproteins, and CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. When a TLR binds to its cognate PAMP, host-cell adaptor molecules such as MyD88, TIRAP and TRIF are recruited, and downstream signaling is initiated. The resulting activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) promotes transcription of a range of genes coding for proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-23, which trigger the production of IL-17 and IL-22 in cell subsets including Th17, γδ T and ILC3.