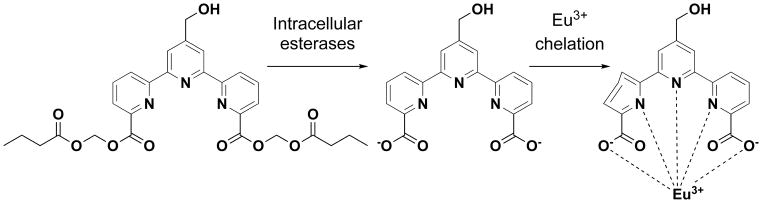
Scheme 4.
Schematic representation of an improved non-radioactive cellular cytotoxicity assay method using a novel terpyridine derivative proligand. When target tumor cells are treated with bis(butyryloxymethyl) 4′-hydroxymethyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-6,6″-dicarboxylate, a newly designed and synthesized terpyridine derivative proligand, it permeates into the target cells, where it is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterases to yield 4′-hydroxymethyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-6,6″-dicarboxylic acid. Because the nascent hydrolyzates are negatively-charged, the ions accumulate in the target cells. When the labeled tumor cells are killed by immune effector cells, the ions are released into the culture medium. Upon addition of Eu3+ to the supernatant, the ion and Eu3+ forms a complex that emits long-life fluorescence under excitation with laser pulses.