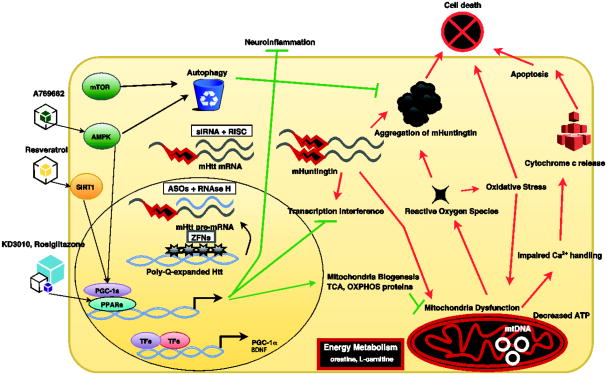
Figure 1. Huntington's Disease therapies directed at intracellular processes.
, A schematic illustration showing various intracellular processes that are perturbed by mutant huntingtin protein and thus high priority targets for therapy development. Note that some therapies are designed to work in the nucleus, others in the cytosol, and some at specific organelles, including especially mitochondria. AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase); SIRT1 (Sirtuin 1); mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin); PPARs (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors); PPARGC1A (PPAR gamma co-activator 1-alpha); OXPHOS (oxidative phosphorylation); TCA (tricarboxylic acid cycle); siRNA (small interfering RNA); RISC (RNA induced silencing complex); ASO (antisense oligonucleotide); ZFPs (zinc finger proteins); TFs (transcription factors); mtDNA (mitochondrial DNA).