Fig. 4.
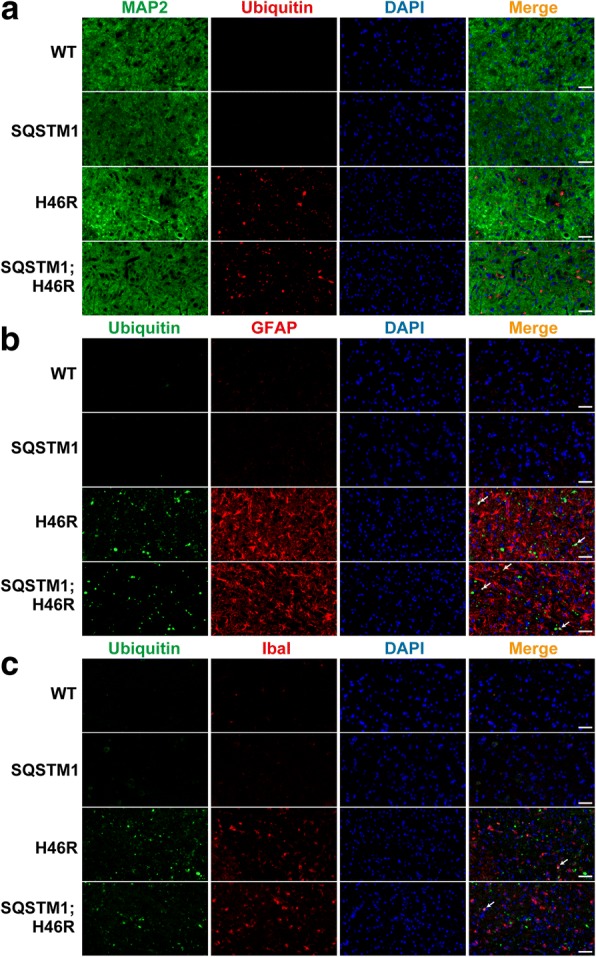
Extensive accumulation of ubiquitin-positive aggregates in the spinal cord from SOD1H46R-expressing mice at end-stage. a-c Representative images of double immunostaining with MAP2 (green; neuron marker) and Ubiquitin (red) (a), Ubiquitin (green) and GFAP (red; astrocyte marker) (b), Ubiquitin (green) and Iba1 (red; microglia marker) (c) in the lumbar spinal cord (L4–5) from wild-type (WT) and SQSTM1 (SQSTM1) at 28 weeks of age, SOD1H46R (H46R) and SQSTM1;SOD1H46R (SQSTM1;H46R) mice at end-stage. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. b Arrows indicate colocalization of ubiquitin-positive aggregates with GFAP-positive astrocytes. c Arrows indicate colocalization of ubiquitin-positive aggregates with Iba1-positive microglia
