Fig. 2.
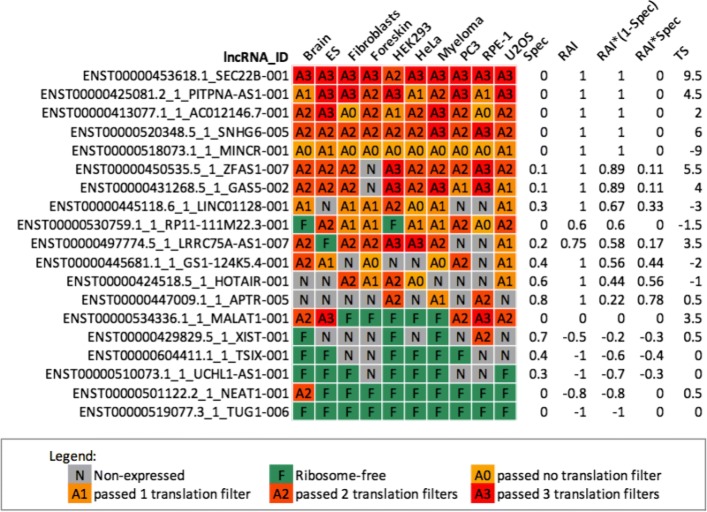
The ribosomal association index (RAI) enables an integrative analysis of ribosome associability of lncRNAs across multiple independent datasets. The table summarizes ribosomal association and translation for selected human lncRNAs. Rows represent lncRNAs, while colored columns denote datasets. For each lncRNA, “N (gray)” and “F (green)” cells correspond to unexpressed and ribosome-free lncRNAs, respectively. “A0” ∼“A3” cells represent the lncRNA containing a putative ORF that passed 0–3 coding filters. The last four columns are statistics that describe the corresponding lncRNAs. Spec is the transcript expression specificity, ranging from 0 (ubiquitous) to 1 (specific). For a lncRNA, RAI is the ribosomal association index across datasets in which this lncRNA is expressed, ranging from -1 (ribosome-free) to 1 (ribosome-associated). RAI * (1 - spec) is a metric to measure the confidence of ribosomal association for a lncRNA that has a broad expression, ranging from -1 (lncRNA was observed as ribosome-free in most datasets) to 1. Conversely, RAI * spec can be used to select ribosome-associated or ribosome-free lncRNAs from the population of tissue-specific lncRNAs. TS can be used with RAI * (1 - spec) to filter the putatively translated lncRNAs. (See Additional file 8 for the complete list of human and mouse lncRNAs)