Figure 2. PCSK9 compartmentalization and function in plasma.
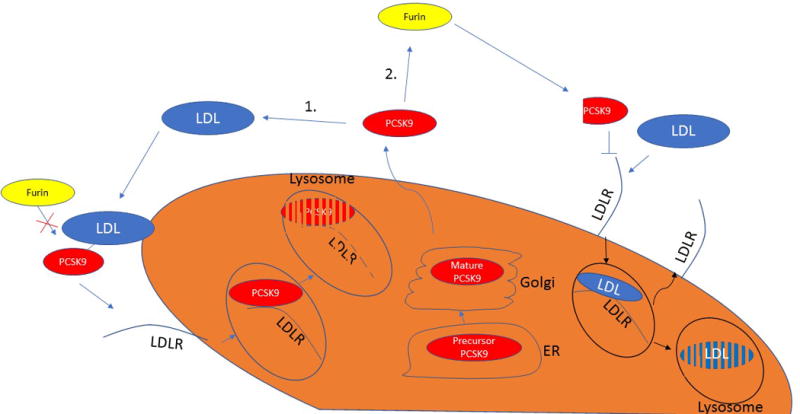
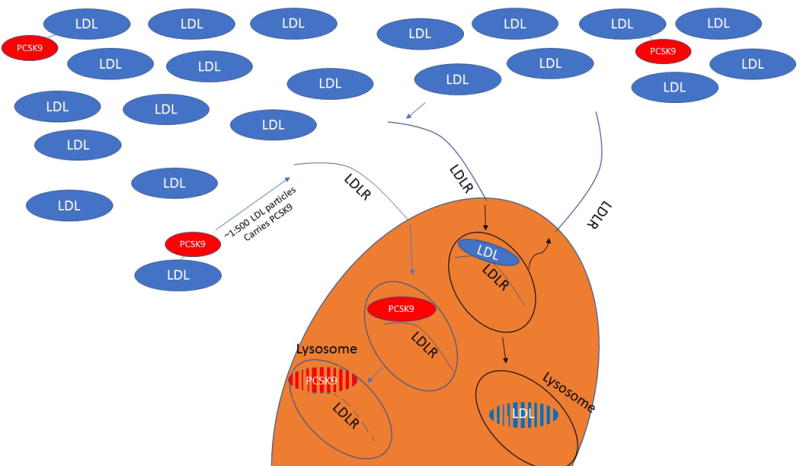
(A) PCSK9 is found in plasma in primarily two monomeric forms; an active form representing the full-length plasma protein and an inactive/less-active shorter fragment, which is a cleavage product of the full length protein by the protease furin. The active PCSK9 is found predominantly on LDL and Lp(a) particles, but not on VLDL or chylomicron remnants. In contrast, the furin-cleaved PCSK9 is not found in association with these apoB-lipoproteins. While it is not clear whether PCSK9 (active or furin cleaved) is found in association with HDL, it was suggested the HDL can inhibit PCSK9 function. (B) PCSK9 is secreted as an active form representing the full-length plasma protein. Upon secretion, PCSK9 can take on one of two fates, which ultimately determines its function. (i) PCSK9 can interact with an LDL particle, which protects PCSK9 from being cleaved by furin and leaves the protein bound to the particle in its active form, or alternatively, (ii) PCSK9 can interact with furin, which leads to the formation of a shorter fragment of PCSK9 that exhibits at least two-fold lower affinity to LDLR with limited ability/inability to degrade it.
PCSK9 = proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; LDL = low-density lipoprotein; Lp(a) = lipoprotein(a); VLDL = very low-density lipoprotein; apoB = apolipoprotein B; HDL = high-density lipoprotein; LDLR = low-density lipoprotein receptor
