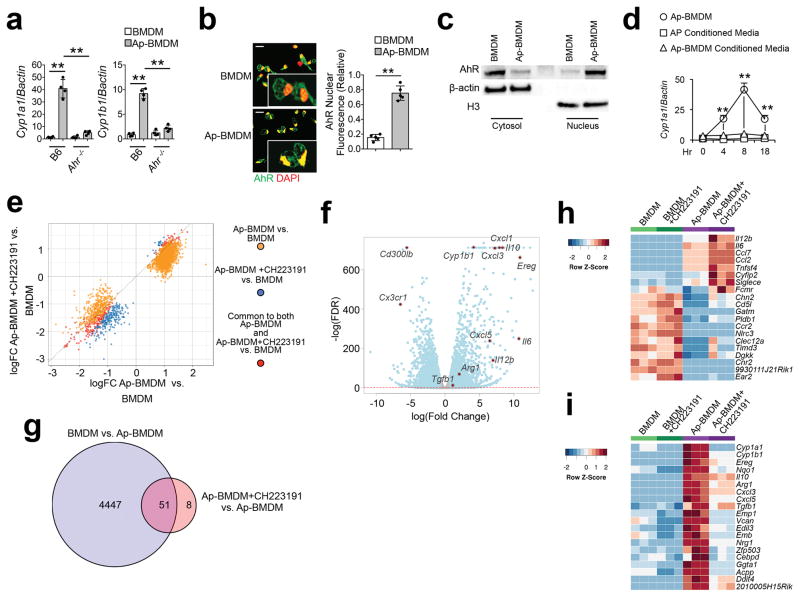
Figure 1. Apoptotic cells activate AhR in resident macrophages driving regulatory polarization.
(a) BMDM of the indicated genotype were co-cultured with B6 apoptotic thymocytes for 8h and indicated mRNA were measured by sqPCR. Data are normalized to expression of β-actin. (b) Nuclear translocation of AhR determined by immunofluorescence 2h after co-culture described in a. Scale bar=20μm. (c) Immunoblot analysis of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts 2h after co-culture as in a. β-actin and histone H3 were used as loading controls for cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts respectively. (d) B6 BMDM were cultured with apoptotic cells as described in a (Ap-BMDM) or cultured in conditioned media from apoptotic thymocyte cultures (Ap Conditioned Media), or from 8h Mϕ/apoptotic cell cultures (Ap-BMDM Conditioned Media) and Cyp1a1 mRNA induction was measured by sqPCR normalized against β-actin. (e) Quadrant plot of DARs identified from ATAC-seq analysis of BMDM versus Ap-BMDM +/− AhR inhibitor. (f) Volcano plot for differential expression based on transcriptome analysis of BMDM versus Ap-BMDM. Red dotted line marks FDR < 0.05. (g) Venn diagram showing significantly differentially expressed genes (FDR < 5%, logFC > ± 0.75) for the comparisons indicated. (h and i) Heat maps showing comparisons of up-regulated h or down-regulated i genes in Ap-BMDM +/− CH223191. For a n=4 and for b and d n=5 biologically independent samples per group +/− standard deviation and **P≤ 0.01 as determined by two sided Student’s t-test. Western blot in c is representative for 3 biologically independent samples and for ATAC- data is representative of 30,000 macrophages per experimental condition. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.