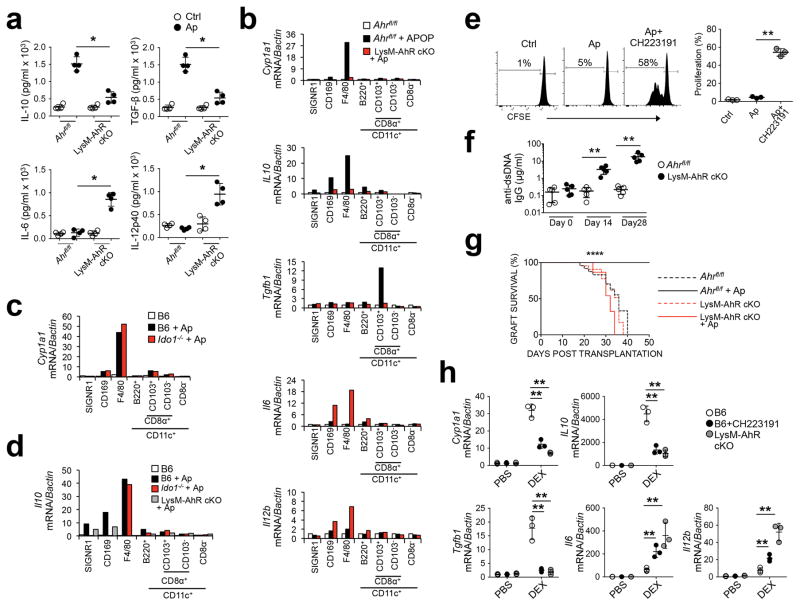
Figure 4. Myeloid AhR is required for apoptotic cell-driven tolerance in vivo.
(a) Whole spleen lysate from mice 4 hours after apoptotic cell challenge (107 i/v) were measured for the indicated cytokines. (b, c, and d) Splenic macrophages and DC were sorted by FACS from mice of the indicated genotype 4 hours after apoptotic cell injection i.v. based on the markers indicated, and message for the indicated mRNA species was determined by sqPCR. (e) B6 mice +/− CH2231191 administration received CFSE-labeled Thy1.1+CD4+ OTII T cells i/v followed by challenge with OVA+ apoptotic cells. 3d later spleens were collected and CFSE intensity was determined by flow cytometry. (f) Mice were injected with apoptotic cells and serum was collected at the indicated time points and total IgG reactive against dsDNA was determined by ELISA. (g) Female mice received 107 male B6 apoptotic thymocytes i.v. and 7 days later received skin allografts from male B6 mice. N=10 mice/group. ****=P<0.0001 determined by log-rank test. (h) Control mice +/− CH223191 and B6.Ahr−/− mice received dexamethasone i.p. (0.2 mg per mouse). 24h later thymus was harvested and processed for quantification of mRNA by sqPCR. For a n=4, e and h n=3 biologically independent samples per group and bars are the mean +/− standard deviation. *=P≤ 0.05, =Pval≤ 0.01 as determined by two-sided Student’s t-test. For b, c, and d bars represent pooled samples from 4 mice/group. All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.