Figure 5.
DHX9 Depletion Triggers R-Loop Accumulation in Response to CPT
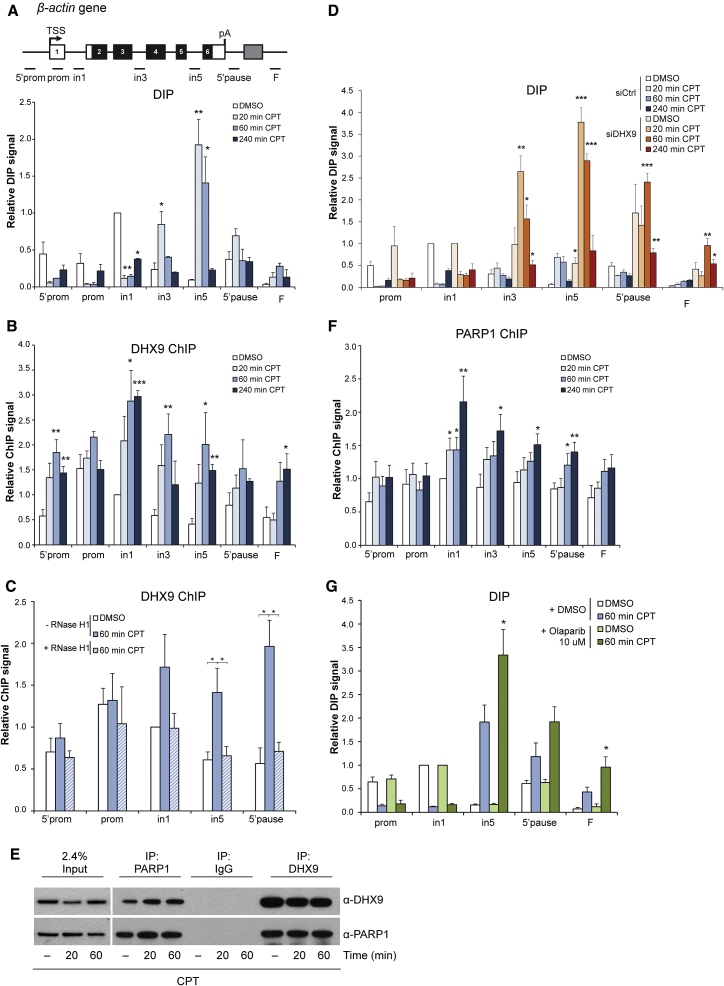
(A, B, and F) Diagram of β-actin gene (A, top), DIP (A, bottom), DHX9 ChIP (B), and PARP1 ChIP (F) in HeLa cells, treated with CPT for the indicated time, on β-actin gene. Values are relative to in1 in the DMSO sample.
(C) DHX9 ChIP in HEK293T cells, transfected with FLAG (−RNase H1) or RNase H1 (+RNase H1) and treated with CPT for 60 min. Values are relative to in1 −RNase H1 in the DMSO sample.
(D) DIP in HeLa cells, transfected with control (shades of blue) or DHX9 #1 (shades of red) siRNA and treated with CPT for indicated time, on the β-actin gene. Values are relative to in1 for each siRNA. The p-value is calculated for the siDHX9 versus the siCtrl sample.
(E) Western blot of IgG2a (negative control), PARP1, and DHX9 IPs in HeLa cells treated with CPT and probed with indicated antibodies. Left: input, right: IP.
(G) DIP in HeLa cells, treated with DMSO (shades of blue) or Olaparib (shades of green) before addition of CPT for 60 min, on the β-actin gene. Values are relative to in1 for DMSO and Olaparib. The pvalue is calculated for the Olaparib + CPT versus the DMSO + CPT samples.
(A–D, F, and G) Bars, means ± SEMs, n ≥ 3.
See also Figures S5 and S6.