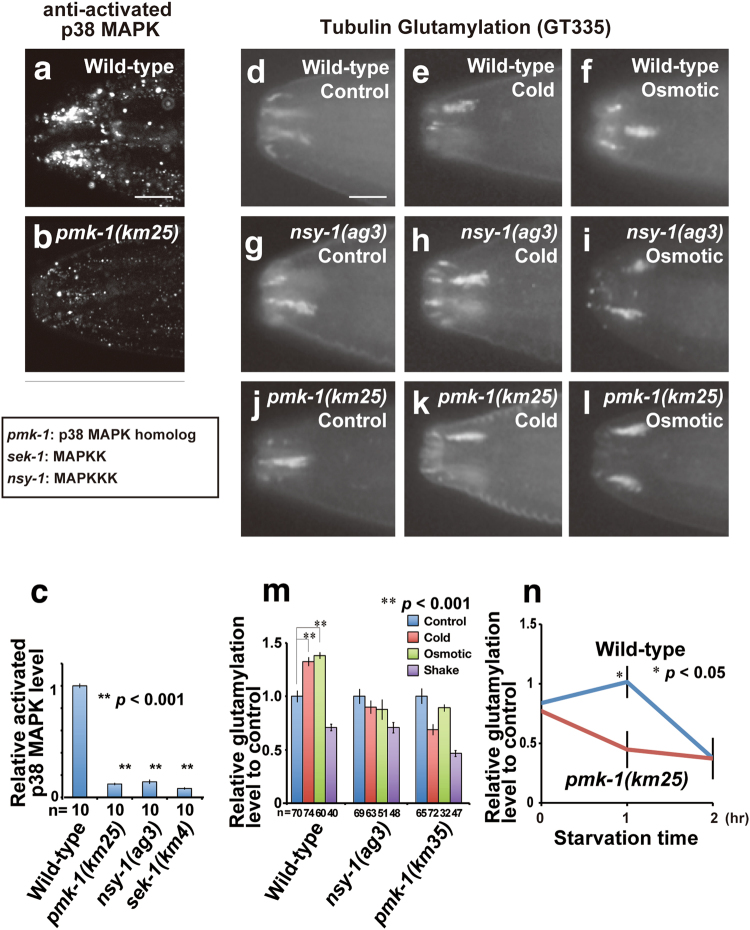
Figure 3.
Modification of tubulin glutamylation is mediated by p38 MAPK signalling. (a–c) Results of the immunohistochemical analysis of activated p38 MAPK-specific antibody in wild-type (a) and a pmk-1 mutant (b). Quantified result of activated p38 MAPK in wild-type and the mutants of members of the p38 MAPK signalling pathway (c). p38 MAPK is activated in sensory cilia in a manner dependent on the upstream kinases in the pathway. (d–l) Results of the immunohistochemical analysis of tubulin glutamylation in wild-type (d–f), pmk-1 (g–i), and nsy-1 (j–l) mutants under control (d, e and j), cold (e, h and k), and high osmotic (f, i and l) conditions. (m) Quantified result of tubulin glutamylation. The glutamylation levels after environmental stimuli were relative values for the control (no environmental stimuli). The enhancement of tubulin glutamylation is dependent on p38 MAPK. Y-axis is the relative glutamylation level to control (no environmental stimuli). Thus, the differences of glutamylation level seen in each mutant background were removed. (n) Time course analysis of tubulin glutamylation after starvation. Bars indicate mean ± S.E. All scale bars = 5 μm. An asterisk (*p < 0.05, Student’s t test) indicates significant difference as compared with the signal intensity before starvation in wild-type (n). Double asterisks (**p < 0.001, Student’s t test) indicate significant difference as compared with the wild-type (c and m). Numbers of animals scored are indicated (c and m, bottom).