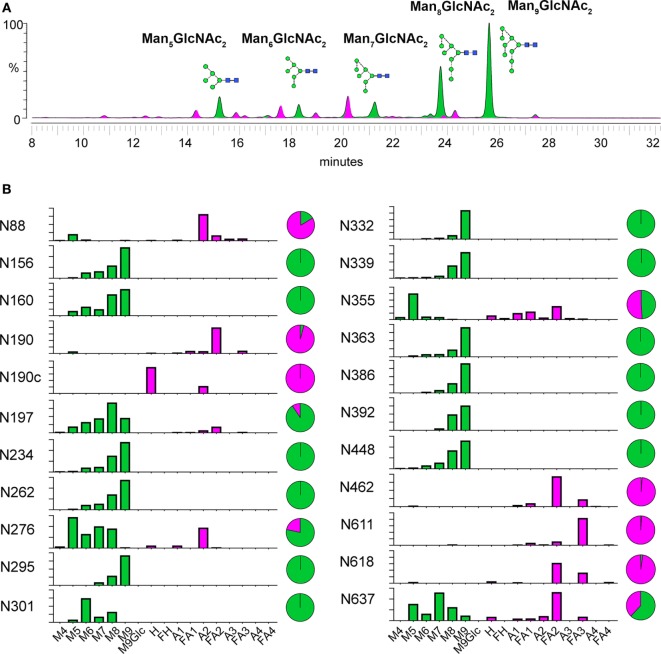
Figure 3.
Glycosylation analysis of BG505 NFL trimers produced in CHO-M cells. (A) Overall glycan composition. Hydrophilic interaction ultra-performance liquid chromatography spectra of fluorescently labeled N-linked glycans released from BG505 NFL produced in CHO-M cells. Oligomannose-type and hybrid-type glycans are colored green and complex-type glycans are colored pink. The corresponding structure for peaks of oligomannose glycans (Man5–9GlcNAc2) are shown and labeled accordingly. (B) Site-specific N-glycosylation analysis. Relative quantification of the microheterogeneity of 22 of 28 BG505 NFL N-glycosylation sites is shown. The trimers were protease digested and analyzed by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. The bar graphs represent the mean of two analytical replicates and the pie charts display the overall abundance of oligomannose-type (green) and complex- and hybrid-type (magenta) glycans. A sample-specific glycan library used as the basis for this analysis is shown in Table S1 in Supplementary Material. Details of glycopeptide peaks identified are shown in Table S2 in Supplementary Material. Identified glycoforms were grouped according to the number of their antennae. The glycan names are as previously described (43) and as follows: Mn = number (n) of mannose residues; An = number (n) of antennae (e.g., A2 = biantennary); Gn = number (n) of galactose residues; H = hybrid residues; F indicates the presence of a core fucose.