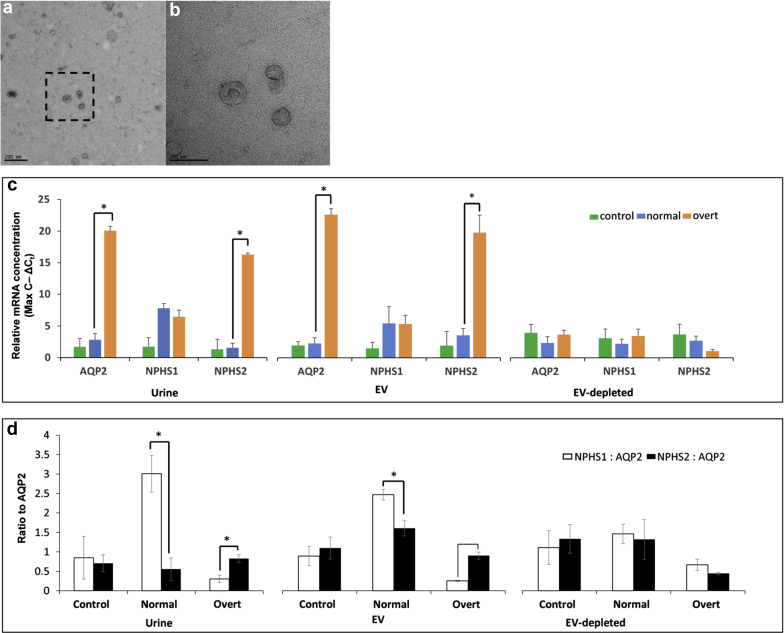
Figure 1.
Isolation of extracellular vesicles (EVs) from urine of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). (a) Scanning electron micrograph of EVs isolated using size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) from urine. Bar in lower left indicates 200 nm for reference. (b) Higher-resolution image from boxed region in (a). Bar in lower left indicates 100 nm for reference. (c) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction results for mRNA kidney markers Aquaporin2 (AQP2), Nephrin (NPSH1), and Podocin (NPHS2) in urine, EV, and EV-depleted (EV-dep) samples for control (green bars, non-T1D), normal (blue bars, T1D nonmicroalbuminuria), and overt (orange bars, T1D overt diabetic nephropathy status) patient samples. Values are represented as the inverse of ΔCt values (maximum number of cycles – ΔCt) to give the linear range, which is directly proportional to the concentration of each mRNA in each sample. (d) The ratio of NPHS1 (white bars) and NPHS2 (solid bars) to AQP2 (NPHS1: AQP2, NPHS2: AQP2) from linear range values in (c) is shown for control, normal, and overt patient samples in urine, EV, and EV-dep samples. Statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05) comparisons are indicated by an asterisk.