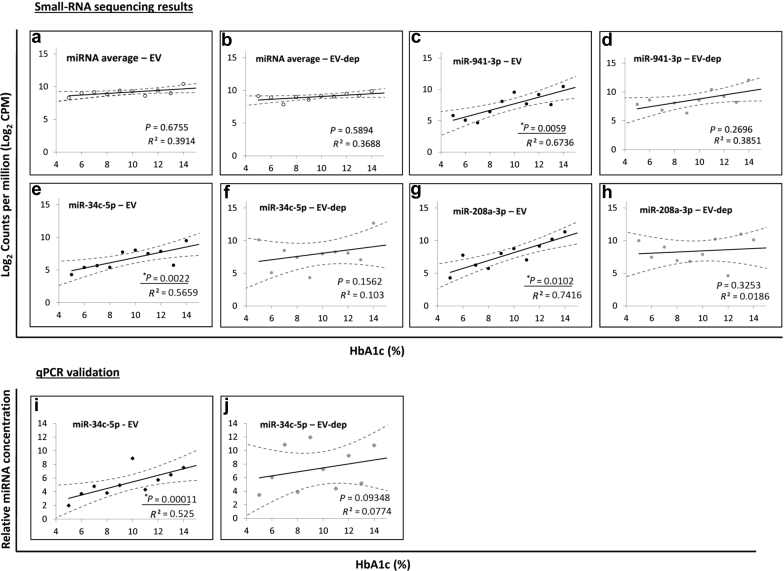
Figure 4.
Extracellular vesicle (EV) microRNAs (miRNAs) that show linear correlation with type 1 diabetes patient plasma glucose (hemoglobin A1c [HbA1c]). Plots of log2 counts per million (CPM) versus patient HbA1c (%) for (a) average of all miRNAs in patient EV samples, (b) average of all miRNAs in patient EV-depleted samples, (c) miR-941-3p in patient EV samples, (d) miR-941-3p in patient EV-depleted samples, (e) miR-34c-5p in patient EV samples, (f) miR-34c-5p in patient EV-depleted samples, (g) miR-208a-3p in patient EV samples, and (h) miR-208a-3p in patient EV-depleted samples. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) results for miR-34c-5p in patient (i) EV and (j) EV-depleted samples. qPCR values are represented as the inverse of ΔCt values (maximum number of cycles – ΔCt) to give the linear range, which is directly proportional to the concentration of each miRNA in each sample. Correlation coefficients (R2 values) and P values are reported in bottom right corners. Statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05) linear correlations are underlined.