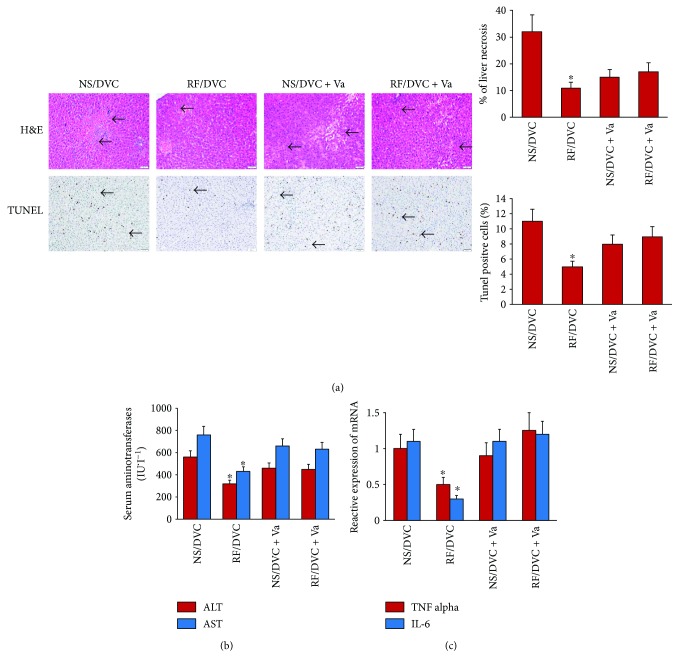
Figure 4.
Microinjection of remifentanil in DVC alleviated hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury but abolished by vagotomy. Rats were divided into 4 groups with or without vagotomy and then injected with 1 μg of remifentanil or normal saline into DVC. Hepatic IR was induced 10 minutes after the treatment above with ischemia for 45 minutes and 120-minute reperfusion. n = 8 in each group. (a) Photograph depicting a typical pattern of focal necrosis (black arrows) after ischemic degeneration of hepatocytes around the central venous area showed that histologic damage was significantly decreased when injected with remifentanil into DVC (RF/DVC) but not in the NS/DVC and RF/DVC + Va groups. Hepatocyte apoptosis determined by TUNEL staining indicated that hepatocyte apoptosis was significantly decreased in the group with DVC injection of remifentanil (RF/DVC) without vagotomy (magnification: 200x; ∗P < 0.05 versus NS/DVC, NS/DVC + Va, and RF/DVC + Va groups). (b) Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were significantly decreased in the group with DVC injection of remifentanil (RF/DVC) than in the NS/DVC and RF/DVC + Va groups (∗P < 0.05 versus NS/DVC, NS/DVC + Va, and RF/DVC + Va groups). (c) TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA expression measured by quantitative real-time PCR were lower in the group injected with remifentanil into DVC (RF/DVC) compared with the NS/DVC and RF/DVC + Va groups (∗P < 0.05 versus NS/DVC, NS/DVC + Va, and RF/DVC + Va groups).