Figure 3.
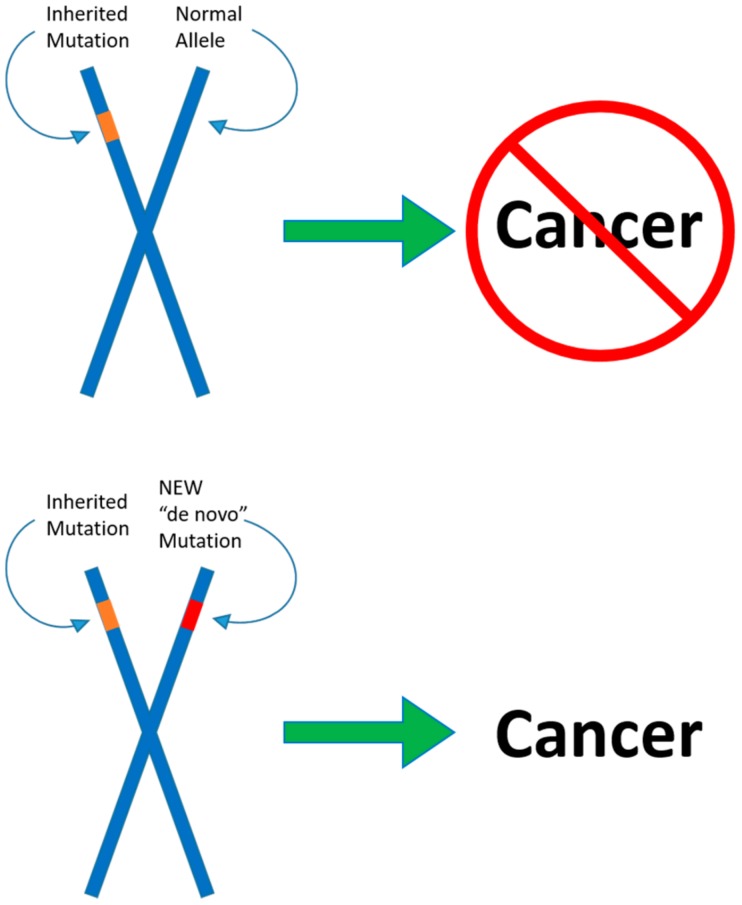
The two-hit hypothesis. One germline mutation in a DICER1 allele predisposes the individual to an increased risk for benign and malignant tumors. A second somatic mutation in the other allele arising during tumorigenesis may lead to malignant rare cancers. While the first mutation by itself is overtly harmless, it only acts in tandem with the second to induce cancerous formation, according to the hypothesis.