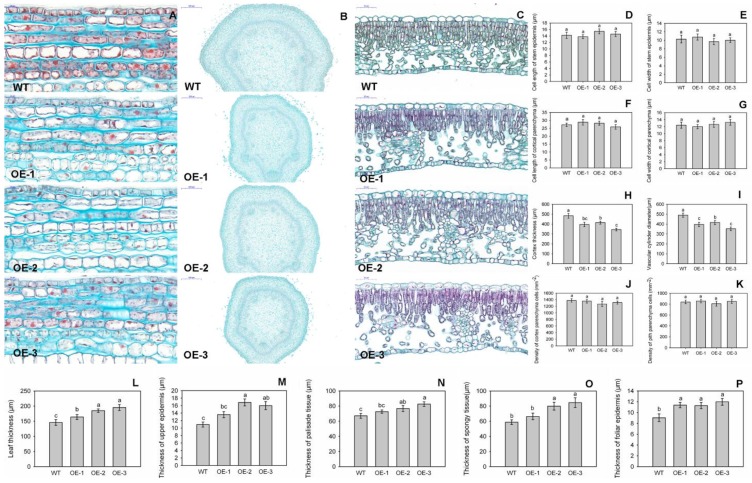
Figure 4.
Anatomical structures of stems and leaves from transgenic and wild-type (WT) plants. Longitudinal paraffin sections (A) and transverse paraffin sections (B) of stems from transgenic and WT plants analyzed using a light microscopy. (C) Transverse paraffin sections of leaves from transgenic and WT plants. Genotypes did not differ significantly in the longitudinal lengths of stem epidermis cells (D), or stem cortical parenchyma cells (E), widths of epidermis cells (F), or stem cortical parenchyma cells (G), cell density of cortical parenchyma cells (J) or pith parenchyma cells (K). However, transgenic plants displayed smaller cortical thickness (H) and smaller vascular cylinder diameter (I), but had thicker in leaves (L), upper epidermis (M), palisade tissue (N), spongy tissue (O), and foliar epidermis (P) when compared with WT. Anatomical structures of stems or leaves were analyzed with four biological repeats. The data are presented as means ± standard deviations. Detailed information on statistics, please see Figure 3.