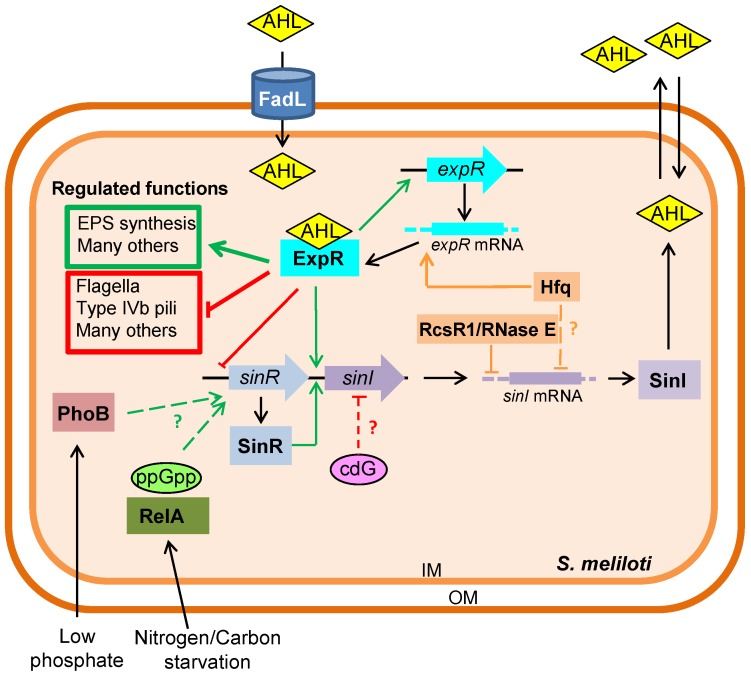
Figure 1.
Model of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of quorum sensing (QS) in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Transcriptional autoregulation of the ExpR/Sin system is shown. N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL)-activated ExpR induces sinI and inhibits sinR. AHL-activated ExpR activates expR expression weakly. Transcriptional activation of sinR expression mediated by PhoB and RelA in response to nutrient limitation is also represented. Cyclic diguanylate (cdG) negatively affects sinI expression and AHL synthesis by an as yet unknown mechanism which is expR independent. Post-transcriptional regulation of the sinI transcript mediated by the RNA chaperone Hfq, RNAse E and the small RNA RcsR1 is shown in orange. See text for more details. The protein FadL that facilitates sensing of the long-chain AHLs produced by S. meliloti is represented. Genes are represented by wide arrows, proteins by rectangles, and second messenger by ovals. Green arrows represent activation; red flat-ended lines indicate repression; orange arrows and flat-ended lines indicate positive and negative post-transcriptional regulations, respectively. Question mark indicates that the mechanism of regulation is unknown. AHL: N-acyl homoserine lactone; IM: inner membrane; OM: outer membrane.