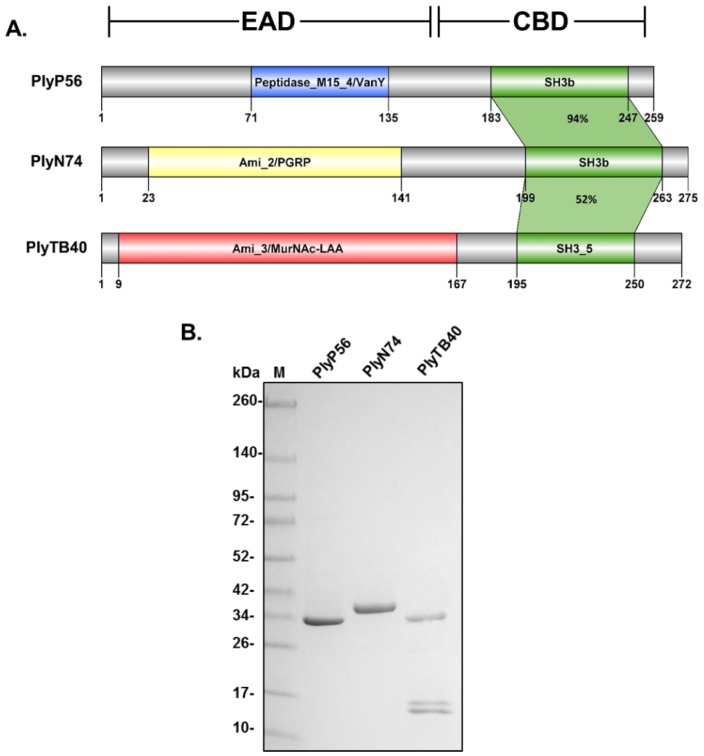
Figure 2.
Bacillus bacteriophage endolysin structural characterization and protein profile. (A) PlyP56, PlyN74, and PlyTB40 contain divergent N-terminal enzymatic active domains (EADs) and conserved C-terminal cell wall binding domains (CBDs). PlyP56 has a Peptidase_M15_4 EAD domain found within the VanY superfamily. PlyN74 has an Amidase_2 EAD domain that is part of the MurNAc-LAA superfamily. PlyTB40 has an Amidase_3 EAD that is also part of the MurNAc-LAA superfamily but lacks homology with the Amidase_2 domain of PlyN74. All three endolysins have similar SH3-family binding domains. Color coding of EADs correspond to Figure 1. (B) Purification of Bacillus phage endolysins. E. coli BL21-(DE3) cells were transformed with a vector encoding recombinant endolysins, grown, and induced with l-arabinose as described under Methods. The recombinant endolysins were purified to homogeneity by nickel affinity chromatography. Protein samples were analyzed for purity by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie blue staining. Lane 1, molecular mass markers as indicated; Lane 2, PlyP56; Lane 3, PlyN74; Lane 4, PlyTB40.