Figure 1.
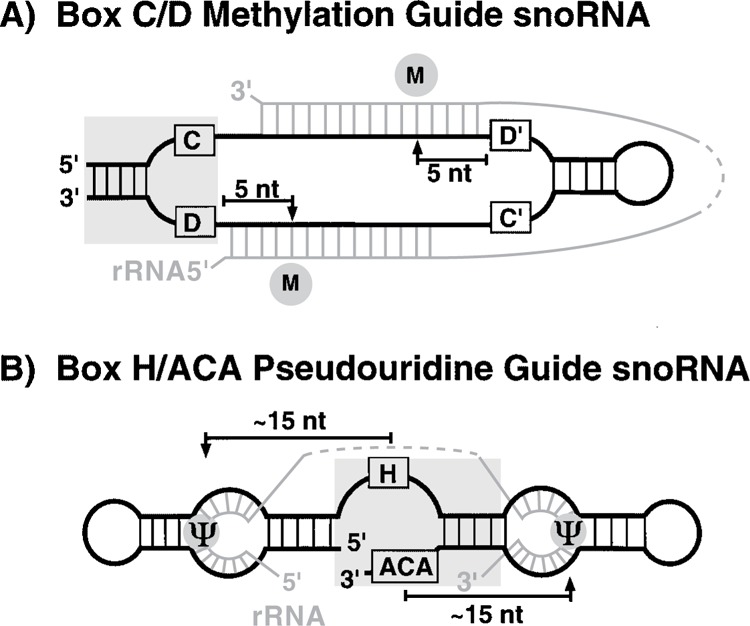
snoRNAs mark rRNA sites for modification. (A) Box C/D guide RNAs direct site-specific rRNA 2′-O-ribose methylation. A box C/ D snoRNA (black) base pairs with one or two complementary rRNA sequences (gray) via complementary sequences (guide sequences) found upstream of box D and/or box D′. The 2′-O-methyl group (M) is always added to the rRNA nucleotide that is paired to the fifth residue upstream of the conserved box D and/or box D′ element. The box C/D motif, a common feature of box C/D snoRNAs, is shaded. (B) Box H/ACA guide RNAs direct the conversion of uridines to pseudouridines. A box H/ACA snoRNA (black) base pairs with complementary rRNA sequences (gray) in one or two loop regions (“pseudouridine pockets”). The target uridine(s) (Ψ) remain unpaired. Pseudouridine formation takes place∼15 nucleotides from the conserved box H or box ACA element. The box H/ACA motif, a common feature of box H/ACA snoRNAs, is shaded.
