Fig. 1.
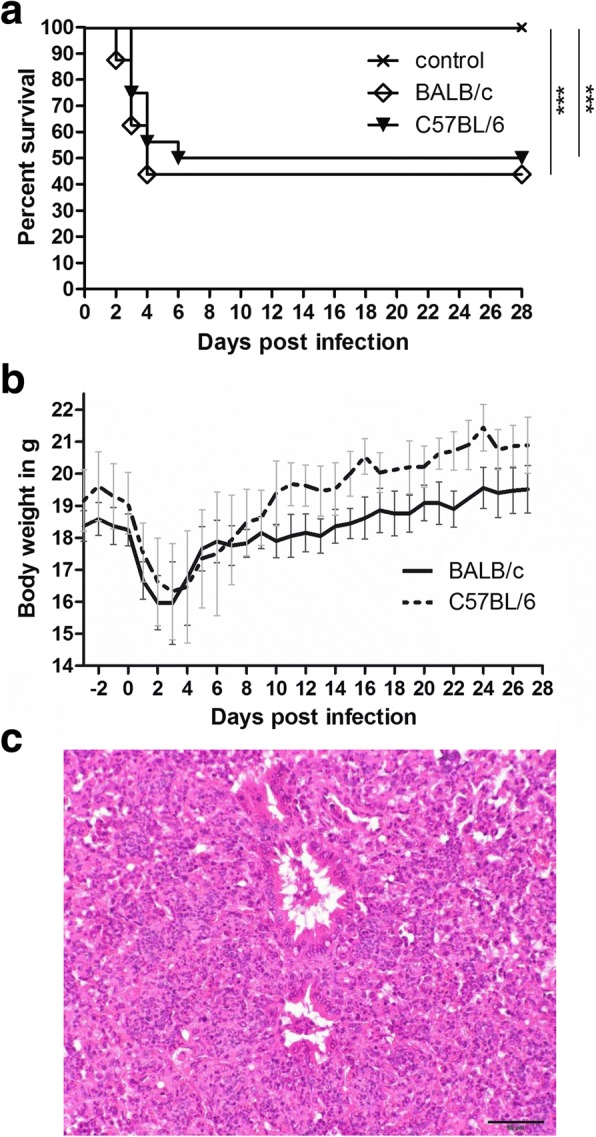
Mortality (a) and body weight (b) of the indicated mice infected with R. pneumotropicus JF4Ni (n = 16 per mouse strain) or treated with PBS as control (n = 10 for BALB/c and n = 9 for C57BL/6, one control died during anaesthesia). Data of contact sentinels are not included. Bronchopneumonia was a main pathology. A multifocal severe catarrhal-purulent bronchopneumonia of a BALB/c mouse 2 days after intranasal infection is shown (c). Alveoli and bronchioles of this mouse were infiltrated with high numbers of neutrophilic granulocytes (200 x magnification). The log rank test was used to analyse differences between the two mice strains and the groups (a)
