Fig. 1.
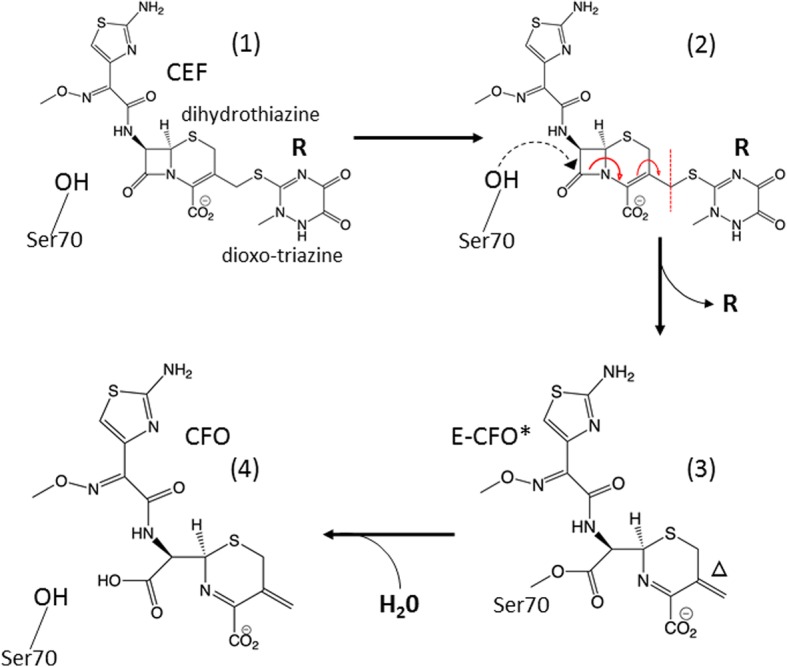
Reaction of β-lactamase with ceftriaxone (CEF). (1) Formation of the enzyme substrate complex by non-covalently binding CEF. (2) Nucleophilic attack of the active site residue Ser-70 results in rearrangement of double bonds and ultimately leads to the opening of the β-lactam ring (blue arrow points to the bond to be cleaved) and the detachment of the leaving group (R). (3) Covalent bond formation between Ser-70 and a shortened species (E-CFO*). Note the double bond ∆. The double bond may react with water to form an alcohol (OH). Evidence for all four intermediate species is found in our experiments. (4) Species (3) is further hydrolyzed from Ser-70 and leaves the enzyme as product
