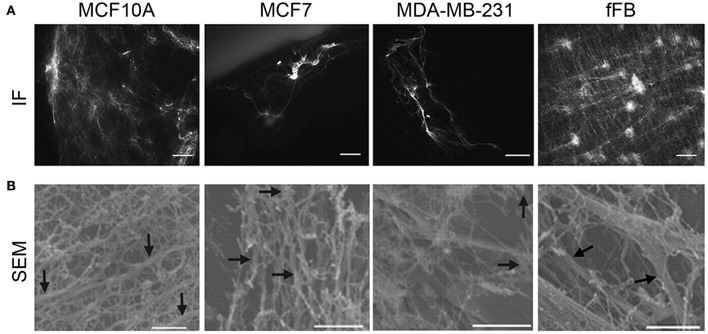
Figure 4.
Correlating cell type and ECM architecture after decellularization. (A) Immunofluorescence (IF, scale bars, 50 μm) staining showed sparse distribution of ECM from multiple breast cancer cell lines, while abundant ECM deposition by human neonatal foreskin fibroblast (fFB). (B) To further visualize the deposition of ECM from the breast cancer cell lines, scanning electron microscopy (SEM, bottom row, scale bars 1 μm) was utilized. MCF10A shows organized, interconnected fiber morphology of ECM; MCF7 has a less organized arrangement of ECM fibers; MDA-MB-231 has a thin, sparse fiber morphology; fFB has a copious monolayer of ECM containing both large and thin-diameter fibers. ECM fibers (0.1- to 0.5 μm diameter) indicated by arrows. (A,B reproduced with permission from Hielscher et al., 2012).