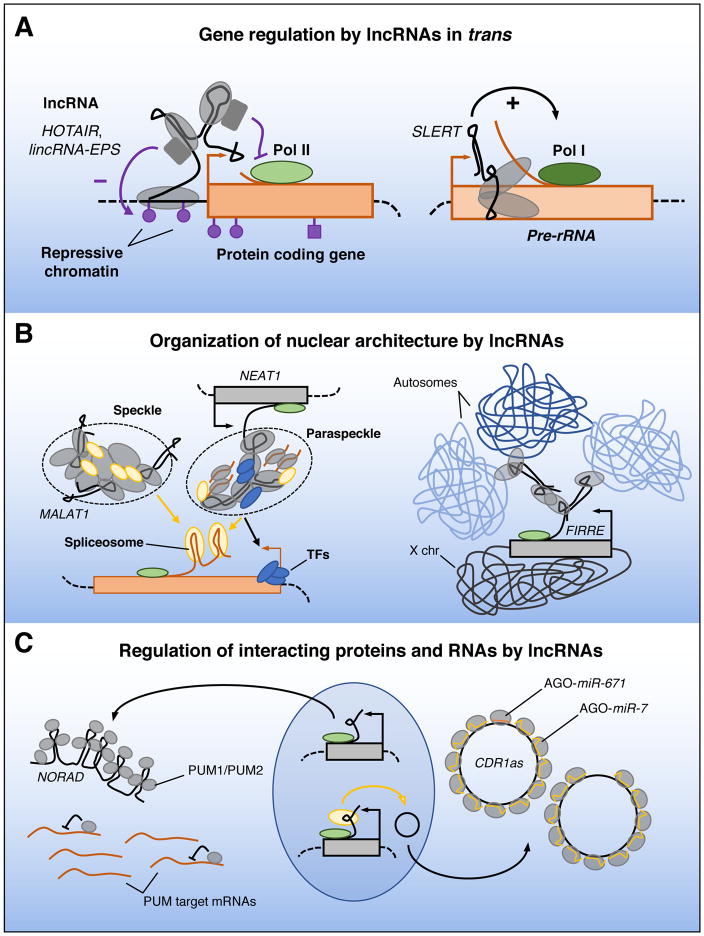
Figure 2. Functions of lncRNAs in trans.
(A) lncRNAs may regulate the expression of unlinked genes by interacting with promoters and enhancers, or other proteins bound to these sites, and influencing chromatin states and RNA polymerase activity. (B) Some lncRNAs are components of dynamic subcellular structures, such as MALAT1 in nuclear speckles and NEAT1 in paraspeckles, and may help to position these structures near actively transcribed genes to facilitate delivery of splicing and transcription factors. lncRNA FIRRE organizes interchromosomal interactions within the nucleus. C) Transacting lncRNAs may regulate the activity of interacting proteins and RNAs in a stoichiometric manner. For example, NORAD binds many molecules of PUMILIO (PUM) proteins, limiting the availability of these post-transcriptional regulators to interact with other targets. CDR1as binds and stabilizes AGO:miR-7 complexes, whereas AGO:miR-671 cleaves the lncRNA. Pol I, RNA polymerase I; X chr, X chromosome.