Figure 9.
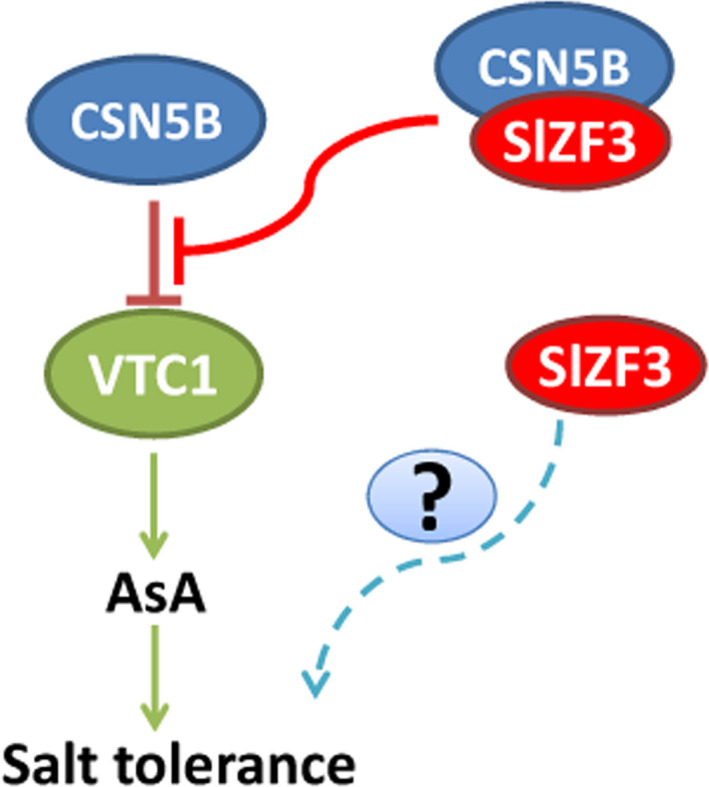
Model for the promotion of AsA accumulation and salt tolerance by SlZF3. CSN5B physically interacts with GDP‐Man pyrophosphorylase (VTC1) and promotes its degradation through the 26S proteasome pathway. SlZF3 and VTC1 competitively bind to CSN5B. This competitive binding inhibits the degradation of VTC1 by CSN5B. VTC1 promotes the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid (AsA). Consequently, SlZF3 promotes the accumulation of AsA and plant salt tolerance by enhancing the reactive oxygen species scavenging capacity of plants. Besides, SlZF3 may also regulate other factors to improve salt tolerance.
