Figure 1.
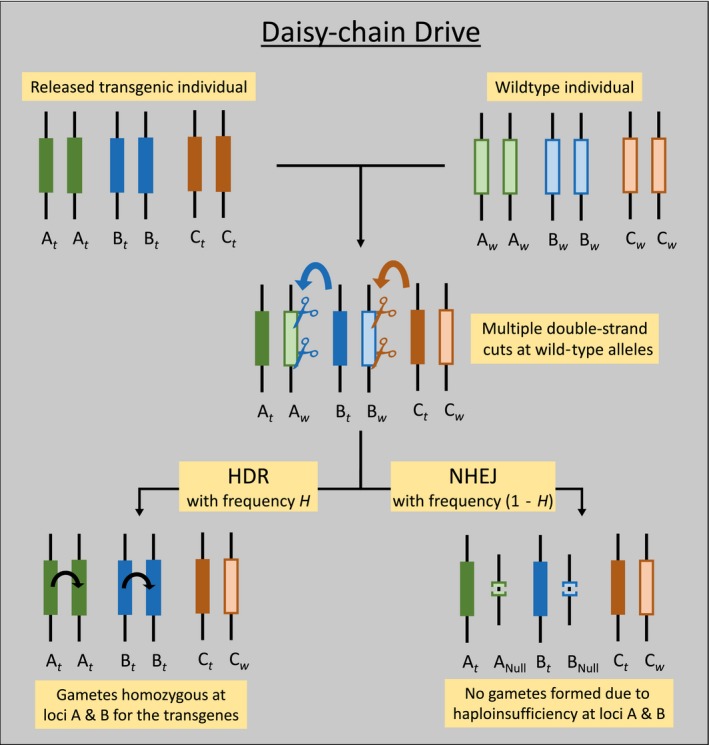
The daisy‐chain drive structure (adapted from Noble et al., 2016) and its mechanism are illustrated. Parental genotypes are shown in the top row. Transgenic alleles are shown with a subscript “t” and with darker colors, while wild‐type alleles have subscript w and lighter colors. The payload gene is located within the A t allele. The transgenic alleles are expressed in the germline cells of the offspring (middle row) resulting in multiple double‐stranded breaks on the wild‐type alleles. Repair through nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) results in deletions on the wild‐type chromosomes and failure of gametogenesis (or production of gametes that fail to produce viable offspring) due to haplo‐insufficiency of the genes, whereas homology‐directed repair (HDR) restores a full complement of the genome and enables successful gametogenesis
