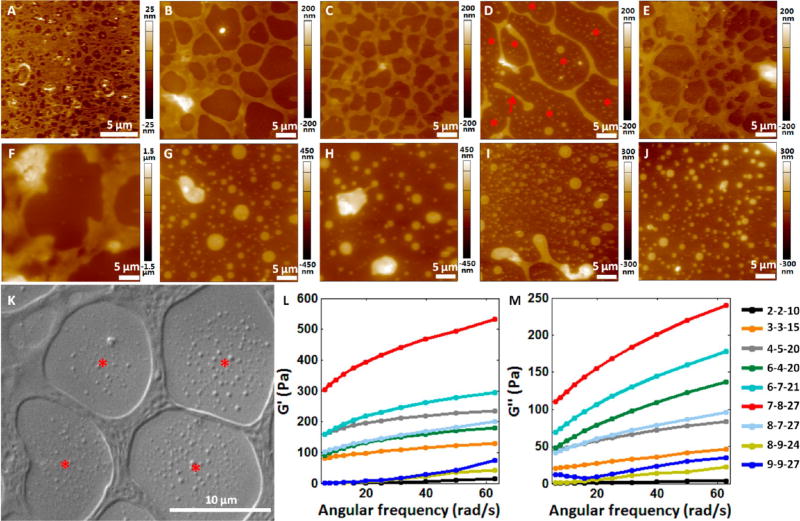
Figure 4.
Structural and mechanical properties of the hydrogels with different component (sodium alginate, gum arabic, Ca2+) ratios. (A–J) AFM height images of the hydrogels with different component ratios. (A) Hydrogel (1-1-5). (B) Hydrogel (2-2-10). (C) Hydrogel (3-3-15). (D) Hydrogel (4-5-20). The red arrow indicates the discretely distributed scaffold. The red asterisks indicate the nanoparticles distributed in the non scaffold areas. (E) Hydrogel (6-4-20). (F) Hydrogel (6-7-21). (G) Hydrogel (7-8-27). (H) Hydrogel (8-7-27). (I) Hydrogel (8-9-24). (J) Hydrogel (9-9-27). (K) SEM image of the hydrogel (3-3-15). The red asterisks indicate the nanoparticles distributed in the non scaffold areas. (L,M) Mechanical properties of the nine hydrogels with different component ratios measured by rheometer. (L) Storage modulus (G′) of the hydrogels. (M) Loss modulus (G″) of the hydrogels.