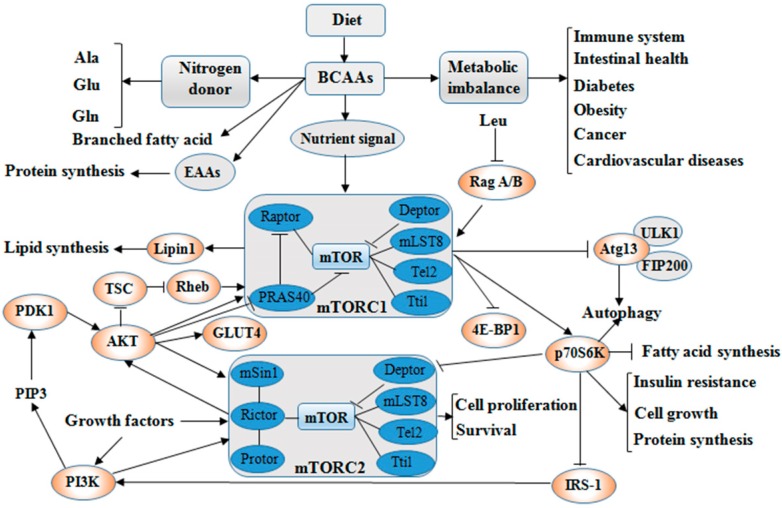
Figure 2.
BCAAs balance and its multiple roles via PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. BCAAs play important role as nitrogen donor for AAs, such as Ala, Glu, and Gln, and also as nutrient signal play critical roles in multiple metabolic functions through special signaling pathway, especially via PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. The metabolic imbalance of BCAAs can cause many health issues, such as diabetes and cancer. Abbreviations: AAs, amino acids; AKT, protein kinase B; Ala, alanine; Atg13, autophagy 13; BCAAs, branched chain amino acids; Deptor, domain containing mTOR interacting protein; 4E-BP1, 4E-binding protein 1; EAAs, essential amino acids; FIP200, focal adhesion kinase-interacting protein 200 kDa; Gln, glutamine; GLUT4, glucose transporter; Glu, glutamate; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; Leu, leucine; Lipin1, phosphatidate phosphatase Lipin1; mLST8, mammalian lethal with Sec13 protein 8 (also known as GβL), mSin1, target of rapamycin complex 2 subunit MAPKAP1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; mTORC1, mTOR complex 1; mTORC2, mTOR complex 2; p70S6K, p70S6 kinase; PDK1, 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; PRAS40, proline-rich Akt substrate 40 kDa; Protor, proline-rich protein; Rag A/B, Ras-related GTP-binding protein A/B; Raptor, regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; Rheb, Ras homolog enriched in brain; Rictor, apamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR; Tel2, telomere length regulation protein; TSC, Tuberous sclerosis; Tti1, TELO2-interacting protein 1; ULK1, UNC51-like kinase 1. (The current understanding of the signaling pathway was based on annotations from the Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)).