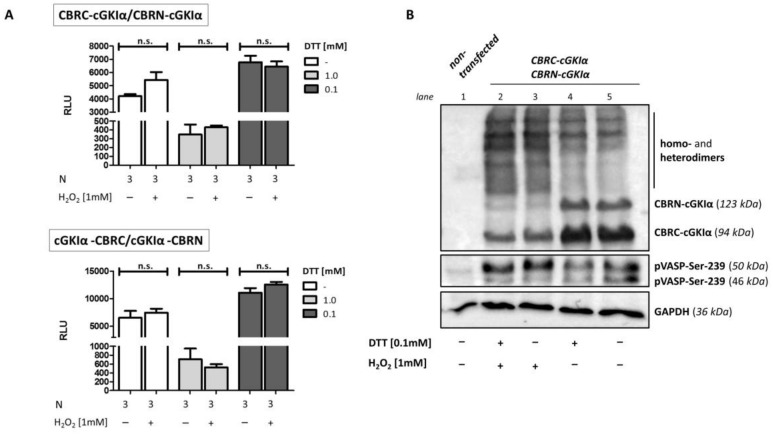
Figure 8.
H2O2-induced cGKIα dimerization. COS7-cells were either seeded in 6-well plates (3.3 × 105 cells/well, (A)) or in 75 cm2 culture flasks and co-transfected with the vector pairs CBRC-cGKIα/CBRN-cGKIα (A,B) or cGKIα-CBRC/cGKIα-CBRN (A) ((A) 1.8 µg DNA, 1:1, B: 22.5 µg, 1:1). 2 h following transfection, dithiothreitol (DTT) (concentration as indicated) was added to medium and cells were either transferred to 96-well plates before incubation (1.0 × 104 cells/well, 24 h, (A)) or directly incubated in cell culture flasks before cell harvest for Western Blot analysis (48 h, (B)). Before cells were stimulated with H2O2 (10 min), medium was again changed to DTT-free medium. (A) Luciferase assay. No change in luminescence signal could be observed in any condition. Data is expressed as mean ± SEM. A non-significant difference was marked as n.s. N = technical replicates. RLU: relative luminescence unit. (B) Western blot. Cells-lysis was performed using a maleimide-containing buffer before separating proteins via 10% SDS-PAGE and subsequent Western blotting. Fusion proteins of cGKIα with CBR-fragments were detected using cGKIα-antibodies, activity of cGKIα was shown using a p-Ser239-VASP antibody, GAPDH served as loading control. No difference in monomer- and dimer band intensity could be identified following reducing compared to non-reducing conditions. Stimulation with hydrogen peroxide caused a shift from monomer to dimer bands in both cases and a slightly increased band intensity of the 50 kDa-band from pVASP-Ser-239, indicating an oxidative activation of cGKIα. VASP: vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein.