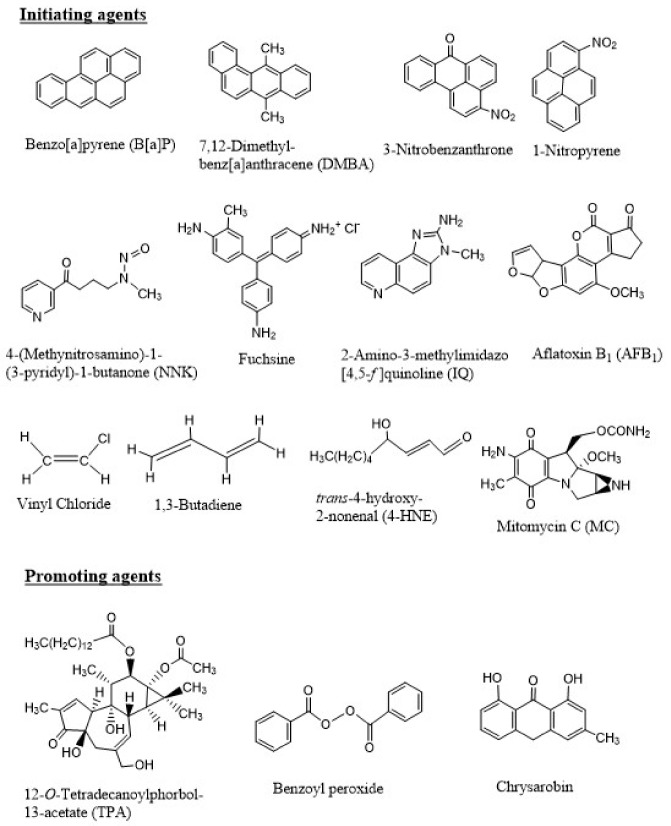
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of a few initiating and promoting agents. The initiating agents shown here include polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) (B[a]P and DMBA, present in soot, coal tar, and many environmental mixtures), nitroaromatic compounds (3-nitrobenzanthrone and 1-nitropyrene, present in diesel exhaust), tobacco-specific nitrosamine (NNK, present in tobacco smoke), an amine salt and a magenta dye (fuchsine), aromatic amine (IQ, formed during cooking of meat), a naturally occurring molecule produced by Aspergillus flavus (AFB1, a food contaminant), industrial chemicals (vinyl chloride and 1,3-butadiene to make the polymer PVC and synthetic rubber, respectively), lipid peroxidation product (4-HNE, produced in cells and tissues of living organisms or in foods during processing or storage), and a chemotherapeutic agent (MC, a toxic drug used to treat upper gastrointestinal cancers). The promoting agents include the phorbol ester (TPA), benzoyl peroxide, and chrysarobin.