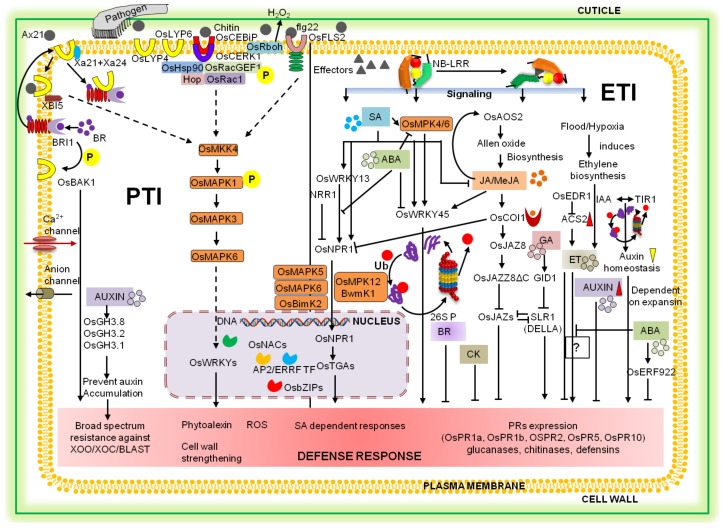
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of rice defense signaling cascades. Following the pathogen perception bypattern recognition receptors(PRRs) and R proteins, the rice plant initiates the diverse set of signaling cascades at different levels (PAMP-triggered immunity (PTI), left side and ETI, right side) involving numerous signal molecules, viz. ROS, NO, MAPKs, CDPKs, phytohormones to trade-off the pathogen invasion. In case of PTI, the host cell recognizes the common molecular pattern associated with most of the pathogens using PRRs (OsLYP6, OsFLS2, OsCEBiP, OsCERK1, Xa21, Xa24) and initiates MAPK kinase cascades (OsMKK4–OsMAPK6) that actually activate host defense responses via various transcriptional regulatory factors (OsWRKYs, OsNACs, OsNPR1, OsTGAs, OsbZIPs). However, PTI is suppressed by pathogen effectors, where they are encountered by the resistance genes (NBS-LRRs) that lead signaling to activate defense responses through phytohormonal activities. The archetypical defense pathways, SA and JA/ET pathways, mainly antagonistic to each other, are responsible for resistance against biotrophs and necrotrophs, respectively. The defense response includes production of PR proteins (glucanases, chitinases, defensins), production of ROS and NO, change in ion fluxes (Ca2+), cell wall strengthening (callose and lignin deposition) to confine the pathogen dissemination and disease development. GA, CK and Auxin act as negative regulators of plant innate immunity. BR prompts or suppresses disease susceptibility based on pathogen lifestyle or colonization. Furthermore, abscisic acid (ABA), well-known in abiotic stress tolerance, plays an ambiguous role, i.e., is both a positive and negative regulator of rice disease resistance based on the type and stage of infection; however, it predominantly actsas a negative regulator. The abbreviations used in the figure above represent viz. SA-salicylic acid; JA-Jasmonic acid, MeJA-Methyl Jasmonate; GB-Gibberellins, BR-Brassinosteroid; ET-Ethylene, CK-Cytokinin; ABA-Abscisic Acid, OsNPR1-Non-expressor of PR1 (NH1, NPR1 homolog1); OsCOI1-Coronatine Insensitive1 (JA receptor); OsJAZ8-Jasmonate ZIM domain protein, HPL3-Hydroperoxide lyase; ACS2-Enzyme for ET biosynthesis (ACC Synthase); OsEDR1-Enhanced Disease resistance 1 (TR1-like kinase); SLR1-slender rice1 (DELLA protein); GID1-encodes GA receptor; BRI1-BR Insensitive 1 (RLK) BR receptor.