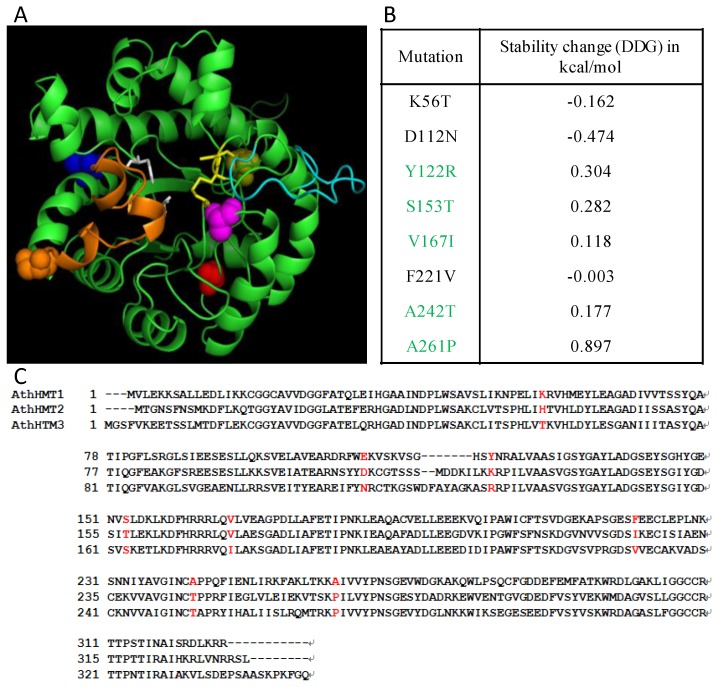
Figure 3.
Potential structural changes in AthHMT1. (A) Overlap of the structural model of AthHMT1 in green, using PyMOL V2.1.1 (https://pymol.org). The different color spheres indicated the predicted key sites of 122 (yellow), 153 (orange), 167 (blue), 242 (magenta), and 261 (red) in AthHMT1; the yellow sticks denote the key sites for the enzyme activity, the white represents three Cys residues (241, 308, and 309 residues) composing a Zn2+-binding center, and the orange, and cyan sheets represent the important loops in the protein, which were reported in E. coli by Li et al [18]. (B) Stability calculations for mutations of AthHMTs performed by the Impact of Non-synonymous mutations on Protein Stability-Multi Dimension (INPS-MD), the ∆G of sites in green were above 0. (C) Consensus sequences for AthHMTs. The sites in red represent type I functional divergence. The cylinders and arrows represent α helixes and β sheets, respectively. The solid lines represent the random coils in the AthHMTs.