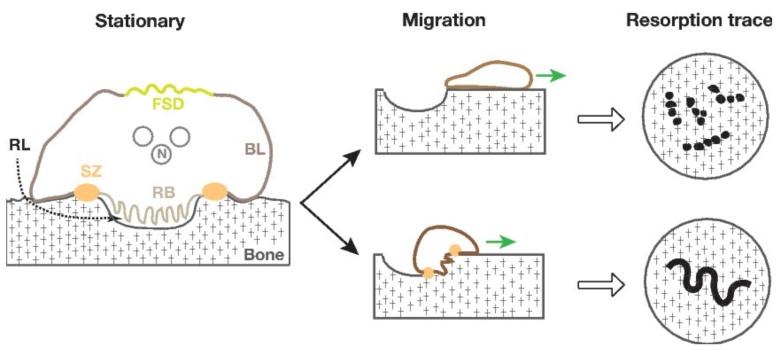
Figure 1.
Polarization of osteoclast during bone resorption. The scheme on the left shows a cross section of the resorbing osteoclast in the stationary mode. The polarization of an osteoclast compartmentalizes its plasma membrane on the bone [9]. The resorption lacune is the space enclosed within the sealing zone, the ruffled border membrane, and the bone. The stationary resorbing osteoclast transits into one of the two migratory modes. The osteoclast stops bone resorption and migrates on bone (upper panel in the middle), or continues bone resorption in the migratory mode (lower panel in the middle). Green arrows indicate the direction of movement. The former mode of osteoclasts forms pit-type resorption traces (upper panel in the right), while the latter produces trail- or trench-type resorption traces (lower panel in the right) [14,15]. The right panels show the resorption traces in a bird’s eye view. BL, basolateral membrane; FSD, functional secretory domain; N, nucleus; RB, ruffled border membrane; RL, resorption lacune; SZ, sealing zone.