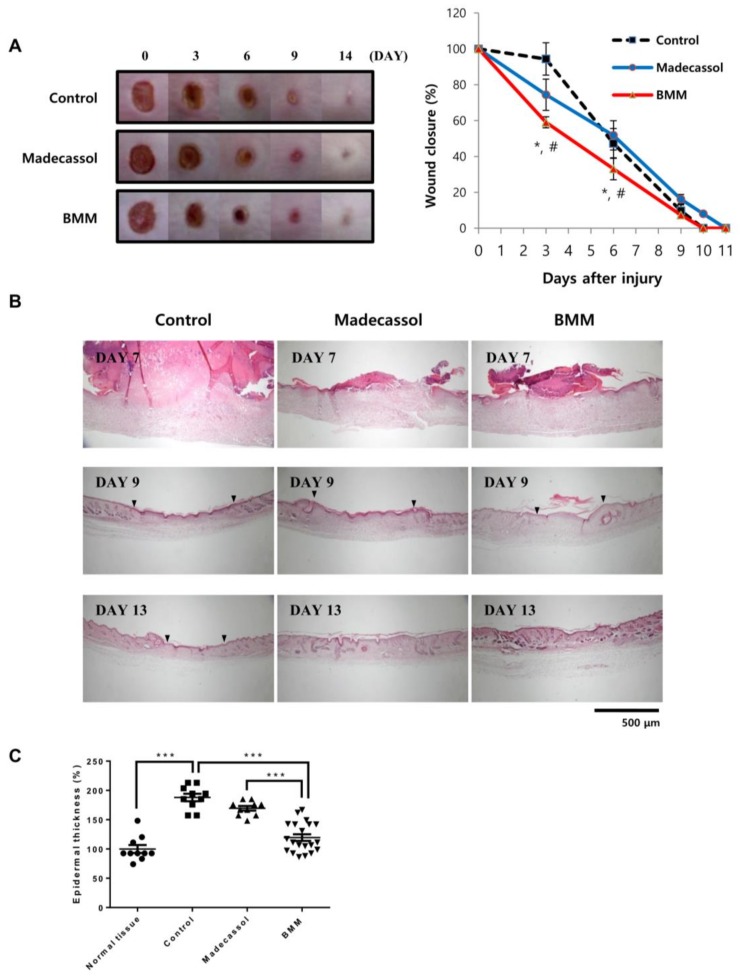
Figure 6.
BMM accelerates wound healing in an in vivo excisional wound model. (A) Wound closure in an excisional wound model over 14 days. Photographs were taken every three days, and wound size was measured using the ImageJ software. ‘Control’ indicates the butylene glycol and “Madecassol” was used for a positive control. The rate of wound closure is shown as a graph. * p < 0.05 as compared to the control, and # p < 0.05 as compared to Madecassol; (B) Hematoxylin&Eosin staining of skin tissue isolated from the wound site on indicated days; (C) Epidermal thickness was measured 13 days after wounding using the Image J program. *** p < 0.001. Dotted line; re-epithelialization, arrowhead; wound edge, and arrow; regenerated skin appendages. Epidermal thickness shown as a graph.