Figure 3.
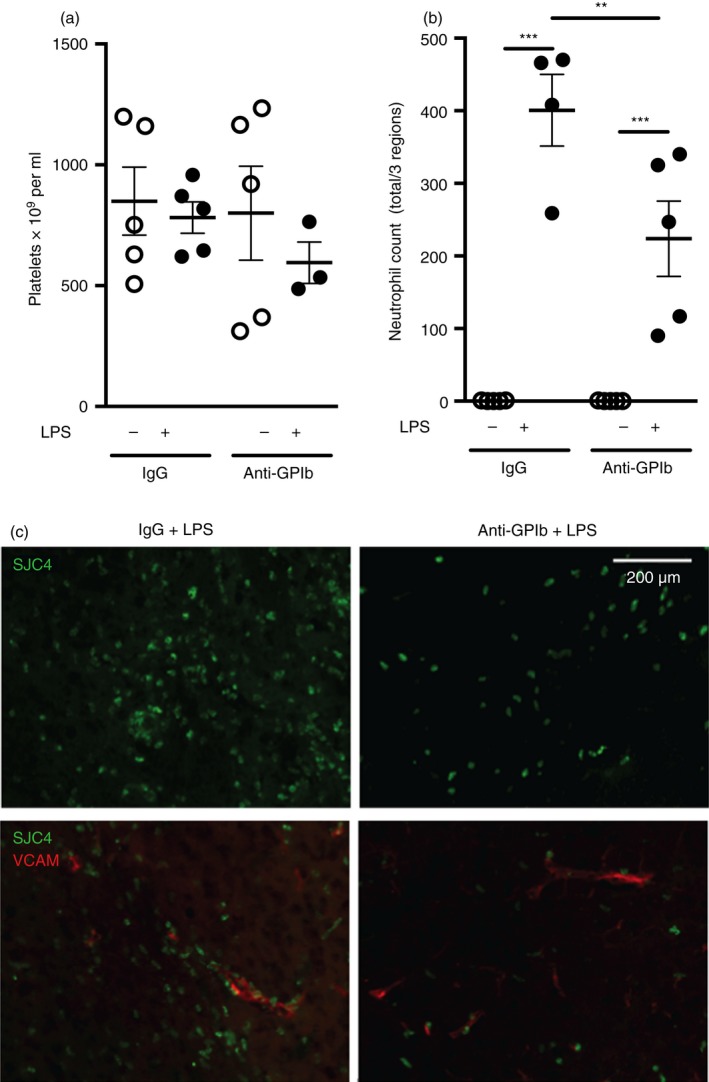
Non‐depleting targeting of platelets reduces neutrophil infiltration to the brain. Anti‐GPIbα antibody or IgG control was administered (4 mg/kg intraperitoneally) 4 hr before lipopolysaccharide (LPS) ‐induced brain inflammation. Anti‐GPIbα antibody had no effect on numbers of circulating platelets compared with IgG‐injected controls (a) yet significantly reduced the number of neutrophils in brain tissue compared with IgG control during inflammation (b). Representative immunofluorescence staining of reduced neutrophil numbers in the brain striatum following LPS injection in the presence of the anti‐GPIbα antibody versus IgG control, which were not accompanied by any change in cerebrovascular activation (vascular cellular adhesion molecule‐1 staining) (c). **P < 0·01, ***P < 0·001; one‐way analysis of variance with Bonferroni's correction. Individual data points are presented as a scatter graph with the mean ± SEM shown. Scale bar = 200 μm. [Colour figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
