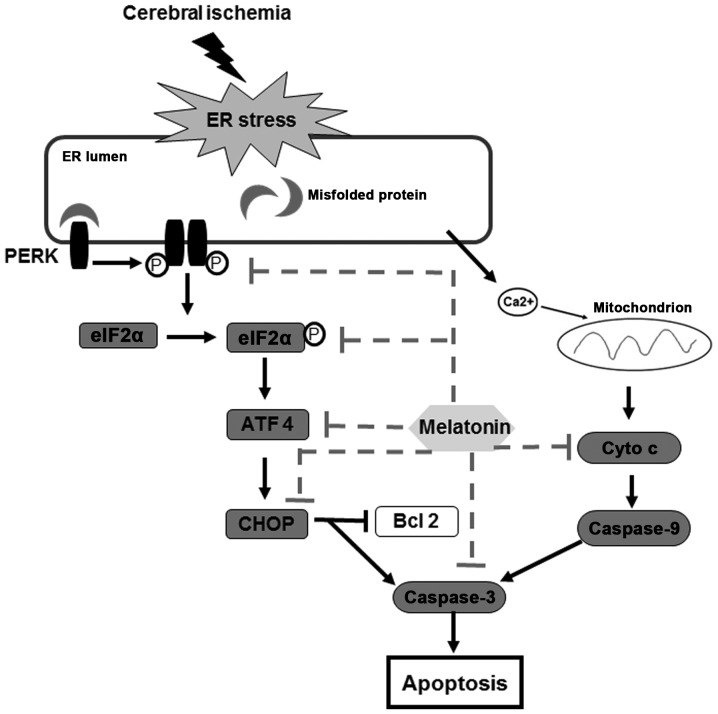
Figure 7.
The mechanisms of melatonin protected neurons against ER-induced apoptosis after cerebral ischemia. Melatonin not only attenuated the phosphorylation of PRKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (p-eIF2α) but also reduced the expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP). At the same time, cytochrome c (Cyto c) was restrained and the expression of caspase-3 was reduced. These results suggest that attenuation of ER stress-induced apoptosis is due to the mechanisms of melatonin.