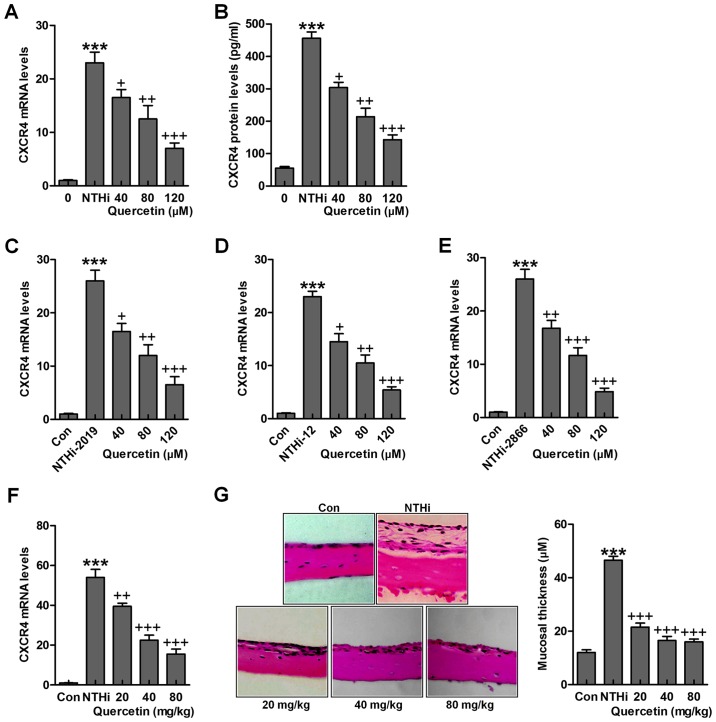
Figure 5.
Quercetin inhibits NTHi-triggered chemokine CXC receptor 4 (CXCR4) activation. Human middle ear epithelial cells (HMEECs) were stimulated with nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) for 6 h, followed by quercetin treatment at different concentrations (40, 80 and 120 µM) for 2 h. Then, (A) CXCR4 mRNA levels (B) and protein levels were evaluated by RT-qPCR analysis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method, respectively. HMEECs were stimulated with NTHi strains (C) 2019, (D) 12 and (E) 2866 for 6 h. Quercetin was administered to cells under different conditions for 2 h. Then, RT-qPCR assay was carried out to investigate CXCR4 mRNA levels. (F) Mice were pretreated with 5×107 CFU NTHi for 6 h, followed by quercetin administration through i.p. at 20, 40 and 80 mg/kg for 2 h. CXCR4 mRNA levels in the dissected middle ear tissue samples were calculated. (G) The representative images of middle ear histophathology in NTHi-treated mice with or without quercetin administration exhibited by H&E staining. The quantification of mucosa thickness is shown. The representative data are shown as SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 vs. the control (Con) group. +p<0.05, ++p<0.01 and +++p<0.001 vs. the NTHi group.