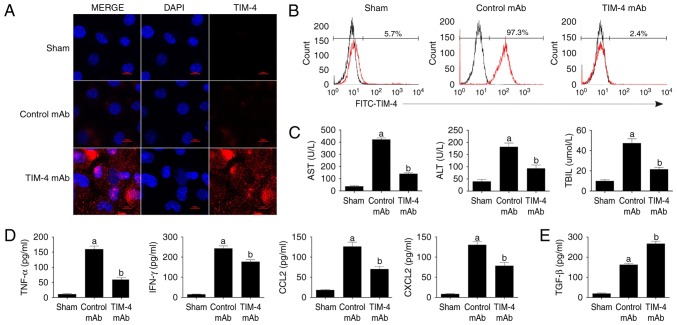
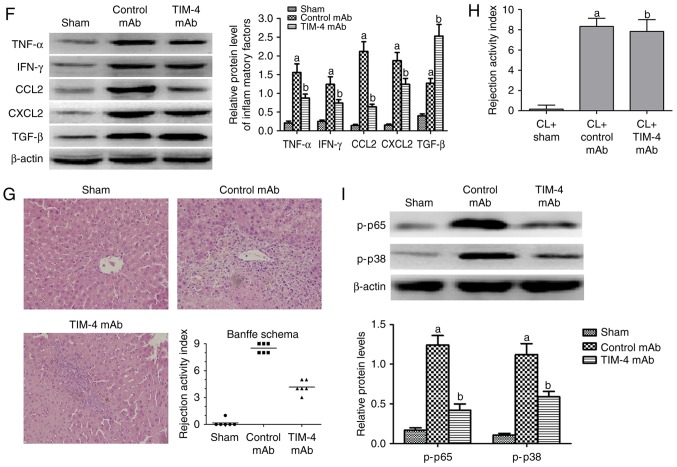
Figure 2.
Blockade of TIM-4 improves hepatic acute reaction response injury and reduces the secretion of inflammatory cytokines. (A) KCs were isolated from mice in the sham, control mAb and TIM-4 mAb groups on day 7 post-surgery. Cells were stained with specific secondary antibodies labeled with tetramethylrhodamine (red) and DAPI (blue) and then examined using laser confocal microscopy (magnification ×800). (B) KCs were isolated from each group and stained with FITC-TIM-4 mAb for flow cytometry. (C) Blood samples were obtained (0.5 ml/mouse) from murine abdominal aortas in each group on day 7 post-surgery. Levels of AST, ALT and TBIL were determined in a clinical biochemical laboratory. (D-F) Levels of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IFN-γ, CCL2, CXCL2 and TGF-β were detected using ELISA and western blotting. (G) Representative micrographs of the pathological damage observed in each group post-transplantation following staining with hematoxylin and eosin (magnification ×400). (H) Donor mice received CL treatment to destroy KCs prior to surgery. orthotopic liver transplantation or sham surgery was subsequently performed and mice were treated either with or without TIM-4 mAb. All mice underwent analysis to determine the RAI score on day 7 following surgery. (I) The expression of key phosphoproteins involved in the NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, including p65 and p38, respectively, were analyzed using western blotting. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. aP<0.05 vs. sham group; bP<0.05 vs. control mAb group. TIM-4, T cell immunoglobulin-domain mucin-domain-4; mAb, monoclonal antibodies; KCs, kupffer cells; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; TBIL, total bilirubin in serum; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; CCL2, chemokine ligand ; CXCL2, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; CL, clondronate liposomes; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.