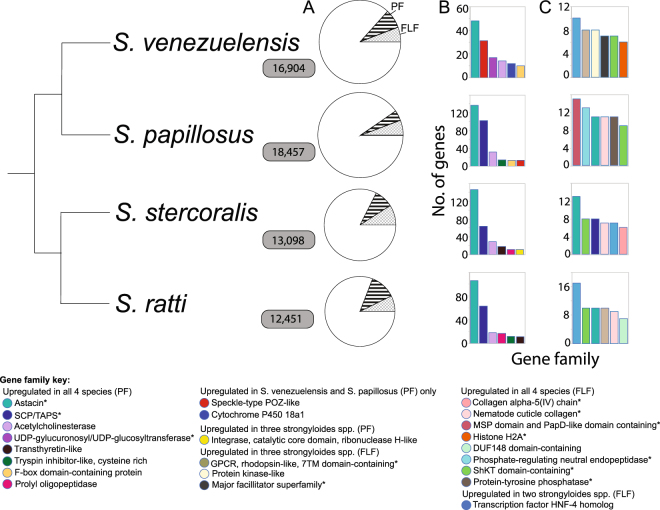
Figure 1.
Differentially expressed genes in parasitic and free-living adult female life cycle stages for four Strongyloides species – S. venezuelensis, S. papillosus, S. ratti and S. stercoralis. (A) Proportion of genes upregulated in the parasitic and free-living adult female life cycle stages of four Strongyloides spp. Total area of the circle is proportional to the total number of predicted protein-coding genes in the genome (total gene number shown in grey boxes). Proportion of genes differentially expressed for a parasitic female (PF) vs. free-living females (FLF) pairwise comparison, determined by edgeR analysis are highlighted (PF – stripes, FLF – squares). (B,C) The six most commonly upregulated gene families are displayed for the parasitic (B) and free-living (C) stages of the life cycle n.b. different y-axis scales. *Represents families where distinct sets of genes belonging to the same family are differentially expressed in both life cycle stages.