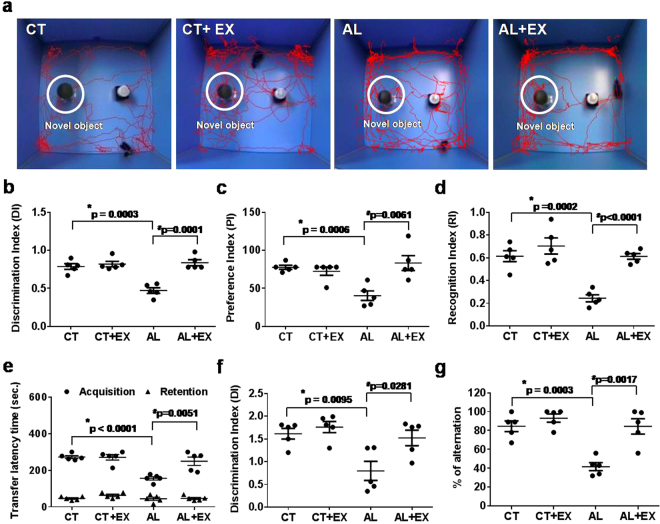
Figure 1.
Effect of exercise on short-term and long-term memory and behavior under alcoholism. (a–d) Short-term memory of mice was assessed by the Novel Object Recognition Test (NORT). Movement patterns of experimental mice assessed by NORT (a). Values of discrimination index (b), preference index (c) and recognition index (d) for experimental groups are shown in scatter dot plots. (e) Similarly, long-term memory of mice was assessed by a Passive Avoidance Task (PAT). Transfer latency time data for the PAT analysis in experimental mice are shown in a scatter dot plot. (f,g) Y-maze data of discrimination index (f) and percentage of spontaneous alterations (g) for experimental groups are shown in scatter dot plots. Data are represented as mean values ± standard error (SE) in 5 independent experiments. *,#p < 0.05 considered significant. *p < 0.05 vs. CT and #p < 0.05 vs. AL group.