Figure 6.
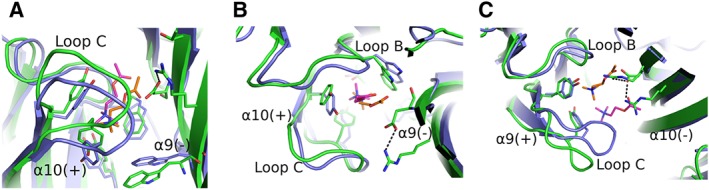
Models of α9/α10 and α10/α9 binding sites. (A–C) Superpositions of the ACh‐bound AChBP crystal structure [AChBP in blue; ACh in orange; PDB ID: 3WIP (Olsen et al., 2014)] with models of the ACh‐bound α9α10 binding sites (α9 and α10 in green; ACh in magenta) (Azam et al., 2015). (A) Side‐view of the α10/α9 interface, showing a similar binding mode for ACh with that in AChBP, although ACh and loop C are shifted upwards. (B) The same as in (A), rotated by 90o, also showing a lateral shift of loops B and C of α10(+) side. The stable salt bridge from the α9(−) side is also shown. (C) Top‐view of the α9/α10 interface, showing an extreme shift of ACh outwards, causing an equal shift of α9(+) loop C. A second arginine from α10(−) side penetrates the binding cavity, forming an uncommon charged environment. All interactions are shown in black dashed lines. The coordinates of all the structures depicted were retrieved from Protein Data Bank (http://www.wwpdb.org), and PyMol (http://www.pymol.org) was used to generate the figures.
