Figure 16.
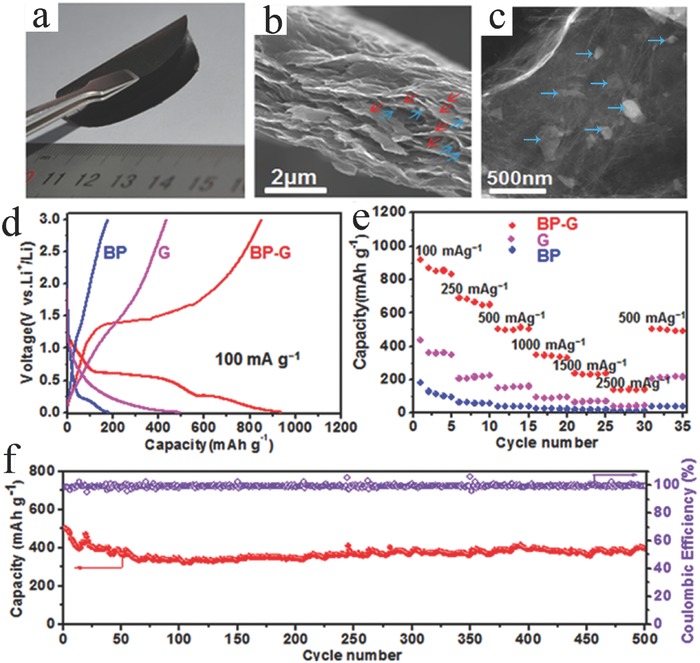
Structure and electrochemical behavior of BP–G hybrid paper. a) Photograph of a BP–G hybrid paper. b) Cross‐sectional view of SEM images of BP–G hybrid paper in panel (a), showing that small BP nanosheets (indicated by blue arrows) are closely contacted with large graphene sheets (indicated by red arrows). c) TEM image of a region of BP–G hybrid paper. d) Second galvanostatic charge/discharge profiles of BP nanosheets, G‐paper, and BP–G hybrid paper electrodes at a current density of 100 mA g−1. e) The rate performance of BP nanosheets, graphene paper, and BP–G hybrid paper electrodes at different current densities. f) The cycling stability and Coulombic efficiency (CE) of BP–G hybrid paper electrode at 500 mA g−1 for 500 cycles after the rate capability test. Reproduced with permission.118
