Figure 1.
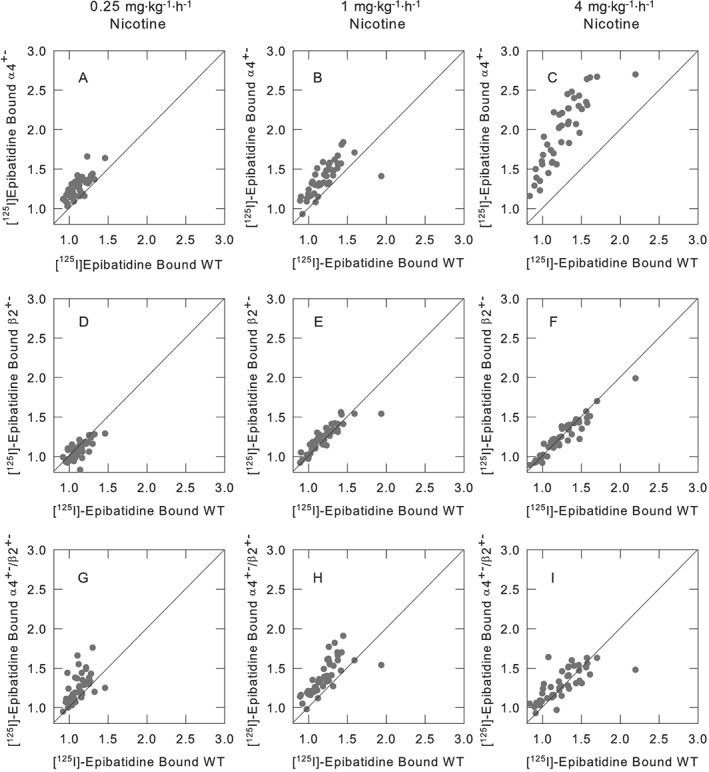
Relative effects of chronic nicotine treatment in mice differing in α4β2*‐expression, compared with the effects in wild‐type mice. nAChR binding sites were measured by quantitative autoradiography of [125I]epibatidine binding for wild‐type, α4+−, β2+− or α4+−/β2+− mice that had been chronically treated with saline, 0.25, 1.0 or 4.0 mg·kg−1·h−1 nicotine for 10 days. Panels (A), (B) and (C) compare the binding for α4+− mice to that of wild‐type. Panels (D), (E) and (F) compare the binding for β2+− to that of wild‐type, and panels (G), (H) and (I) compare the binding for α4+−/β2+− to that of wild‐type for each of the brain regions listed in Supporting Information Table S1 to demonstrate the effect of partial gene deletion of the α4 and/or β2 nAChR subunits. The panels illustrate the relative changes in the density of [125I]epibatidine binding following chronic nicotine of α4+−, β2+− or α4+−/β2+− mice to the changes measured for wild‐type mice. Each point has been normalized to the binding measured for the saline infused of the same genotype. Lines of unit slope are included.
