Figure 3.
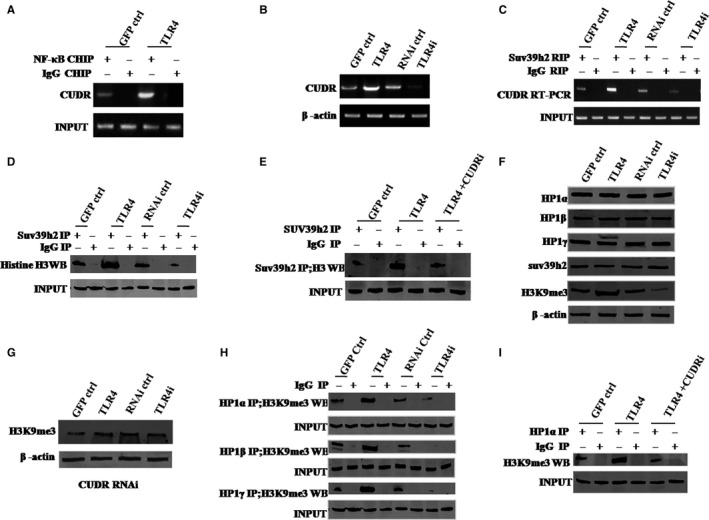
TLR4 increases interplay between HP1 isoforms and H3K9me3 via CUDR. A, Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with anti‐NF‐κB followed by PCR with CUDR promoter primers. IgG ChIP served as negative control. B, RT‐PCR analysis of CUDR mRNA. β‐Actin served as internal control. C, RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) with anti‐SUV39 h1 followed by RT‐PCR with CUDR promoter primers. IgG RIP served as the negative control. D, Co‐immunoprecipitation (Co‐IP) with anti‐SUV39 h2 followed by Western blotting with antihistone. IgG IP served as the negative control. Western blotting with anti‐SUV39 h2 served as INPUT. E, Co‐IP with anti‐SUV39 h2 followed by Western blotting with antihistone H3. IgG IP served as negative control. Western blotting with anti‐SUV39 h2 served as INPUT. F, Western blotting with anti‐HP1α, anti‐HP1β, anti‐HP1γ, anti‐H3K9me3, anti‐SUV39 h2. β‐Actin served as an internal control. G, Western blotting with anti‐H3K9me3 (four hLCSC lines with CUDR being depleted). β‐Actin was the internal control. H, Co‐IP with anti‐H3K9me3 followed by Western blotting with anti‐HP1α, anti‐HP1β and anti‐HP1γ. IgG IP served as negative control. Western blotting with anti‐HP1α, anti‐HP1β, anti‐HP1γ served as INPUT. I, Co‐IP with anti‐H3K9me3 followed by Western blotting with anti‐HP1α. IgG IP was used as negative control. Western blotting with anti‐HP1α as INPUT. Each value was presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Mean ± SEM. **P < .01; *P < .05. For all Western blotting, we repeated the experiments for three times. We measured grey value of the bands for quantification. Each value was presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (Student's t test)
